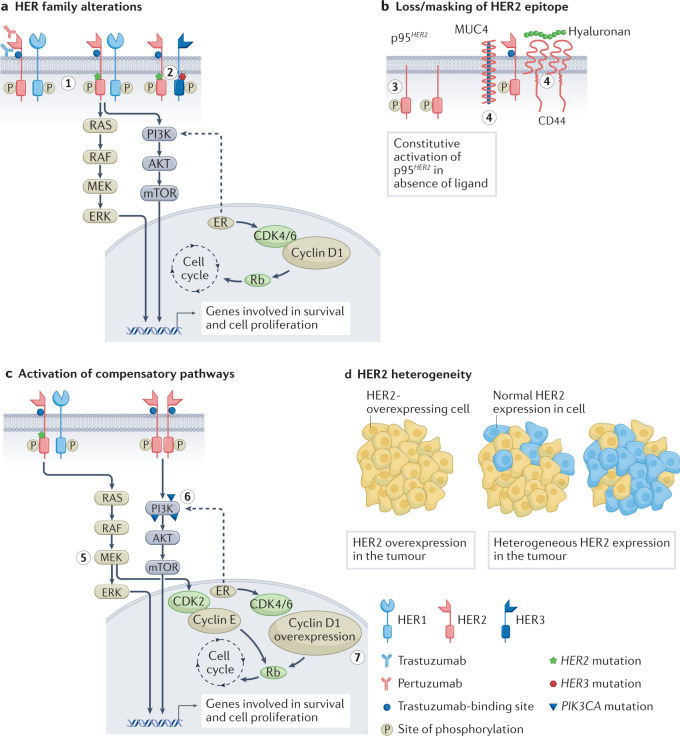
Fig. 2. Select mechanisms of HER2-targeted resistance.
a, Mutations and/or alterations in the HER family of receptors that lead to activation of downstream signalling pathways. (1) Mutations in HER2 leading to P13K–AKT and RAS–MAPK pathway activation. (2) Co-occuring mutations in HER2 and HER3 leading to PI3K–AKT pathway activation. b, Loss of HER2 extracellular domain in cells overexpressing p95HER2 receptor. Masking of the trastuzumab-binding site on HER2 owing to overexpression of mucin 4 (MUC4) and CD44–polymeric hyaluronan complex. (3) p95HER2 overexpression. (4) MUC4 overexpression and CD44–polymeric hyaluronan complex. c, Activation of compensatory pathways. (5) Mutations in HER2 promote MEK–ERK signalling, which activates CDK2 kinase. (6) PIK3CA mutations lead to P13K–AKT pathway activation. (7) Cyclin D1 gene overexpression leads to resistance to anti-HER2 therapies. d, Heterogeneous expression of the HER2 receptor in tumours leads to decreased sensitivity to HER2-targeted therapies that are dependent on overexpression of HER2. ER, oestrogen receptor.