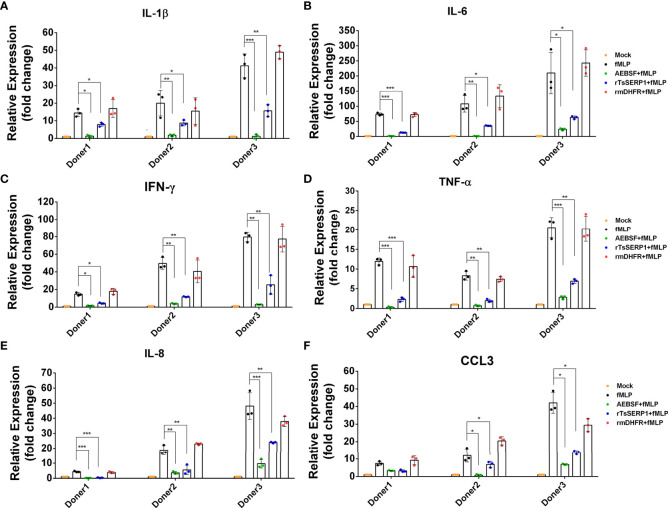
Figure 5.
rTsSERP1 suppresses the transcription levels of cytokine and chemokine mRNAs in human neutrophils. Neutrophils were treated with 10 µg/ml of rTsSERP1 or an irrelevant control (rmDHFR) for 1 h prior and then stimulated with 100 nM of fMLP for 4 h. Thereafter, the cells were collected for RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis for IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), IFN-γ (C), TNF-α (D), IL-8 (E), and CCL3 (F) transcripts. The transcription level of each target was normalized to its own housekeeping gene level [glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)] and then compared with the untreated control (media only) to calculate the relative fold change. The bar charts show the data of three different donors. The results are presented as mean ± SD. The experiments were performed in triplicate with three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni multiple comparison test were used for statistical analysis: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. The treatment conditions were included media alone (Mock), only fMLP induction (fMLP), fMLP induction and AEBSF treatment (AEBSF+fMLP), fMLP induction and rTsSERP1 treatment (rTsSERP1+fMLP), fMLP induction and irrelevant control (rmDHFR) treatment (rmDHFR+fMLP).