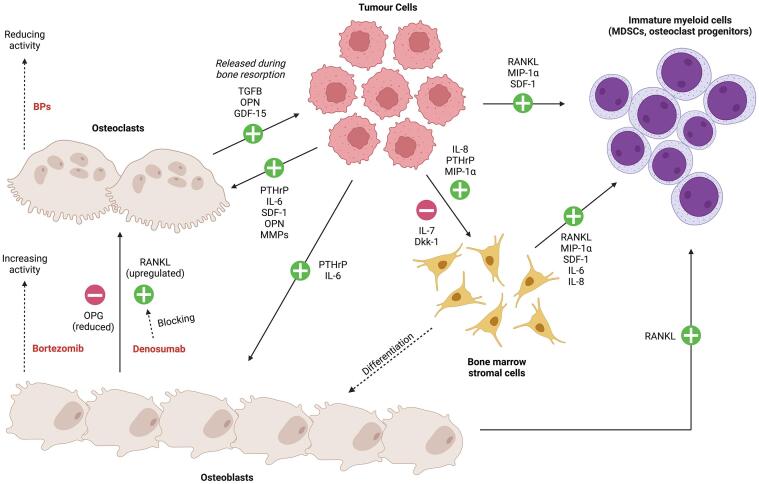
Fig. 1.
Interactions of tumor cells and drug activities with osteoblasts, osteoclasts bone marrow stromal cells and immature myeloid cells. The schematic incorporates points of drug intervention including bisphosphonates (BPs) to reduce osteoclastic activity [49]; Denosumab a neutralizing antibody inhibitor of RANKL that suppresses osteoclastogenesis [50]; and first-in-class proteasome inhibitor (PI) bortezomib that can increase vitamin D receptor (VDR) signaling and markers of osteoblast differentiation [51]. Notably, no therapeutic approach will eliminate the lytic bone lesions caused by MM and can still have progression of skeletal disease if the osteolytic lesions are left untreated [36].