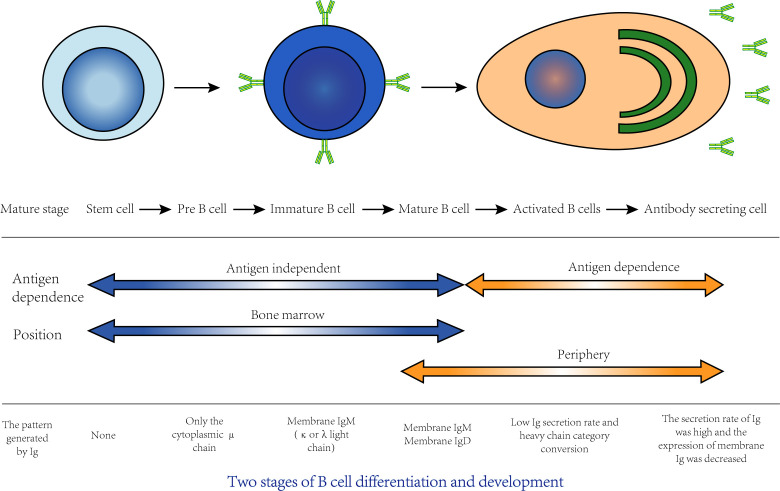
Figure 3.
The differentiation and development of B cells can be divided into two stages: central development and peripheral development. Central development: Stem cells in bone marrow go through the stage of pre-B cells and immature B cells and finally develop into mature B cells, which is also known as the antigen-independent stage of B cell development. This process is closely related to bone marrow hematopoietic microenvironment. Cytokines and adhesion factors in bone marrow stroma are key factors involved in development. Peripheral development: Mature B cells migrate to peripheral immune organs. If it is stimulated by antigen, B cells will proliferate, differentiate into plasma cells and secrete specific antibodies, which is also known as the antigen-dependent period of B cell development. Most of these activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells that secrete specific antibodies, and a few differentiate into memory B cells.