Figure 2.
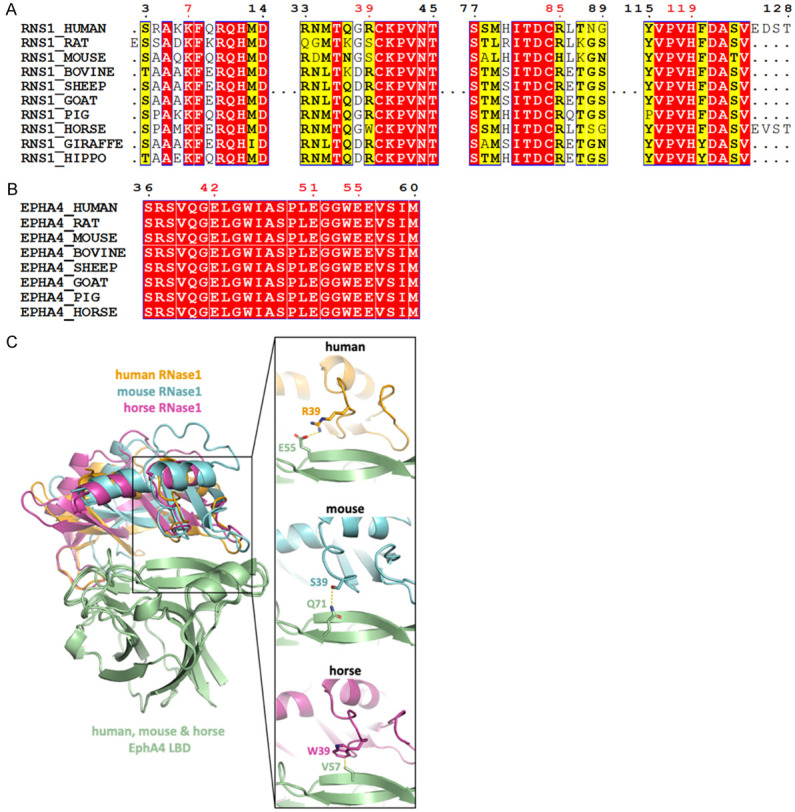
Residues forming salt bridges in the RNase1/EphA4 LBD complex are highly conserved. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of RNase1 among mammals. Sequences from UniProt [51] are RNS1_HUMAN (P07998), RNS1_RAT (P00684), RNS1_MOUSE (P00683), RNS1_BOVINE (P61823), RNS1_SHEEP (P67927), RNS1_GOAT (P67926), RNS1_PIG (P00671); RNS1_HORSE (P00674); RNS1_GIRAFFE (P00662) and RNS1_HIPPO (P00672). Sequence alignment produced by Clustal W [52] and drawn with ESPript [53]. Identities are boxed in red. Similar residues are written with black bold characters and boxed in yellow. Residues number 7, 39, 85 and 119 that are involved in EphA4-binding are labeled in red. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of EphA4 among mammals. Sequences from UniProt are EPHA4_HUMAN (P54764), EPHA4_RAT (D3ZZK3), EPHA4_MOUSE (Q03137), EPHA4_BOVINE (E1BER5), EPHA4_SHEEP (W5QGB9), EPHA4_GOAT (A0A452G0A9), EPHA4_PIG (F1SR66) and EPHA4_HORSE (F7AJ26). Sequence alignment is generated and labelled as in (A). Residues number 42, 51 and 55 that are involved in RNase1-binding are labeled in red. (C) AF2Complex prediction of mouse (cyan) and horse (magentas) RNase1/EphA4 LBD complexes. Superimposition of three complexes showing the salt bridge (R39/E55) in human (orange) is replaced by the hydrogen bond (S39/Q71) and hydrophobic interaction (W39/V57) in mouse and horse, respectively.
