Figure 5.
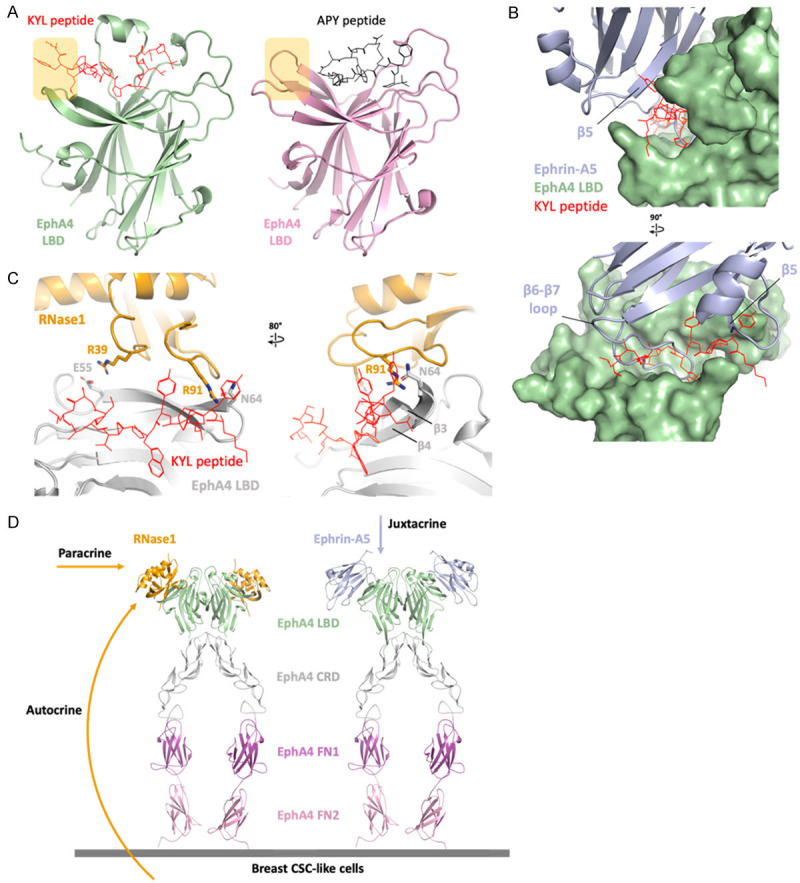
EphA4 inhibitors blocks ephrin and RNase1. A. Linear peptide KYL (red) and circular peptide APY (black) occupied the ephrin-binding site of EphA4 (AlphaFold model in green and crystal structure, PDB ID: 4W50, in pink). The extended region of the KYL peptide is indicated by yellow square. B. Superimposition of ephrin-A5/EphA4 LBD and KYL/EphA4 LBD. Surface representation of EphA4 (green) showing the KYL peptide (red) occupied the ephrin-A5 (light blue)-binding pocket. The KYL peptide blocks the β6-β7 loop as well as β5 of ephrin-A5. C. Superimposition of RNase1/EphA4 LBD and KYL/EphA4 LBD. The KYL peptide (red) blocks the hydrogen bond between R91 of RNase1 (orange stick) and N64 of EphA4 LBD (gray stick). This steric hindrance changed the conformation of β3-β4 of EphA4 and may also disrupt the salt bridge R39/E55. D. Docking the RNase1 (orange)/EphA4 LBD complex to the ephrin-A5 (light blue)/EphA4 extracellular region (ECR) complex (PDB ID: 4M4R) on the basis of the EphA4 LBD to demonstrate the role of RNase1 in paracrine/autocrine signaling. EphA4 ligand binding domain (LBD), cysteine-rich domain (CRD), fibronectin type III repeat 1 (FN1) and fibronectin type III repeat 2 (FN2) are colored in green, gray, magenta and pink, respectively.
