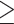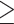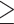Table 2.
Odds ratio of poor cognitive performance for various BMI (or BFP, WC, WHR) categories compared to the healthy BMI (or BFP, WC, WHR) group ( P -values with false discovery rates < 5% are shown in bold)
| Definition of obesity | Male participants | Female participants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio 1 | 95% C.I. | P-value | Odds ratio1 | 95% C.I. | P-value | |
| General obesity defined by BMI 2 | ||||||
|
Underweight (yes vs. no) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 |
0.822 | [0.406, 1.508] | 0.554 | 0.814 | [0.563, 1.146] | 0.254 |
|
Overweight (yes vs. no) 24 kg/m2 < = BMI < 27 kg/m2 |
1.128 | [0.963, 1.322] | 0.135 | 1.031 | [0.920, 1.155] | 0.600 |
|
Obesity (yes vs. no) BMI > = 27 kg/m2 |
1.158 | [0.966, 1.385] | 0.111 | 1.099 | [0.966, 1.250] | 0.150 |
|
General obesity defined by BFP (yes vs. no) 3 BFP BFP |
1.111 | [0.955, 1.290] | 0.171 | 1.035 | [0.920, 1.165] | 0.569 |
|
Abdominal obesity defined by WC (yes vs. no) 4 WC WC |
1.168 | [1.018, 1.340] | 0.027 | 1.214 | [1.091, 1.351] | 3.9E-4 |
|
Abdominal obesity defined by WHR (yes vs. no) 5 WHR WHR |
1.233 | [1.061, 1.436] | 0.007 | 1.221 | [1.094, 1.364] | 3.9E-4 |
1 In all logistic regression models, I adjusted for ten covariates: age, smoking status (yes vs. no), drinking status (yes vs. no), regular exercise (yes vs. no), chronic disease status (yes vs. no), depression status (yes vs. no), blood pressure level, total cholesterol, fasting glucose, and educational attainment (1, 2, …, or 7)
2 Reference group: the healthy weight group (18.5 kg/m2 < = BMI < 24 kg/m2).
3 Reference group: BFP < 25% for males; BFP < 30% for females
4 Reference group: WC < 90 cm for males; WC < 80 cm for females
5 Reference group: WHR < 0.90 for males; WHR < 0.85 for females