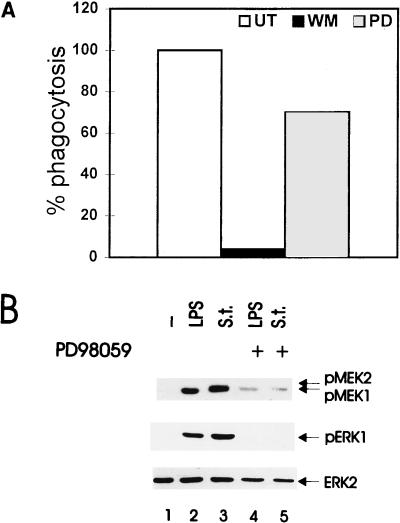
FIG. 6.
Effects of MEK inhibitor PD98059 on the ability of BAC-1.2F5 macrophages to phagocytose Salmonella (A) and on Salmonella- and LPS-stimulated activation of ERK (B). (A) Macrophages were either pretreated with PD98059 (PD; 50 μM, 60 min) or wortmannin (WM; 100 nM, 20 min) or left untreated (UT). Cells were infected with Salmonella (MOI of 25) and allowed to phagocytose for 30 min. Cells were then washed three times with PBS, and fresh medium containing gentamicin (50 μg/ml) was added for a further 60-min incubation to kill residual extracellular bacteria. Phagocytosis was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. Assays were carried out in triplicate. The phagocytic activity of untreated macrophages was set at 100%. (B) Quiescent BAC-1.2F5 cells were pretreated with PD98059 (50 μM, 60 min) and either infected with Salmonella (S.t.; MOI of 25) or stimulated with LPS (1.5 μg/ml) for 15 min prior to solubilization. The presence of phosphorylated MEK and ERK was detected by immunoblotting with the corresponding antibodies. An anti-ERK blot is shown as a loading control.