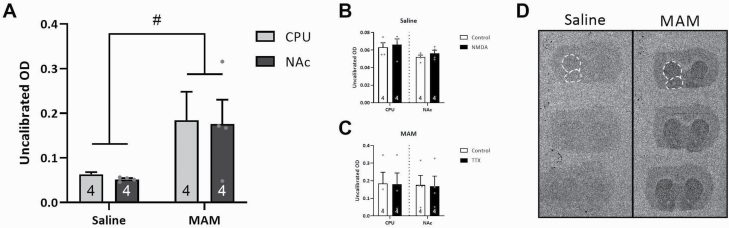
Fig. 2.
Dopamine synthesis capacity in the striatal subregions of MAM-treated rats was significantly elevated. [3H]DOPA ex vivo autoradiography studies indicated a significant increase in dopamine synthesis capacity in the caudate putamen (CPU) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) of MAM-treated rats when compared with saline-treated controls (A), which was not influenced by intrahippocampal injections of NMDA in saline-treated controls to acutely activate the vHipp (B), and TTX in MAM-treated rats to acutely inhibit vHipp activity (C). Representative sections in saline- and MAM-treated rats depicting increased granular accumulation in the striatum of MAM-treated rats (D). White dotted lines indicated subregions that were analyzed. # denotes a significant main effect of MAM. P = .013. Note: MAM, methylazoxymethanol acetate; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate.