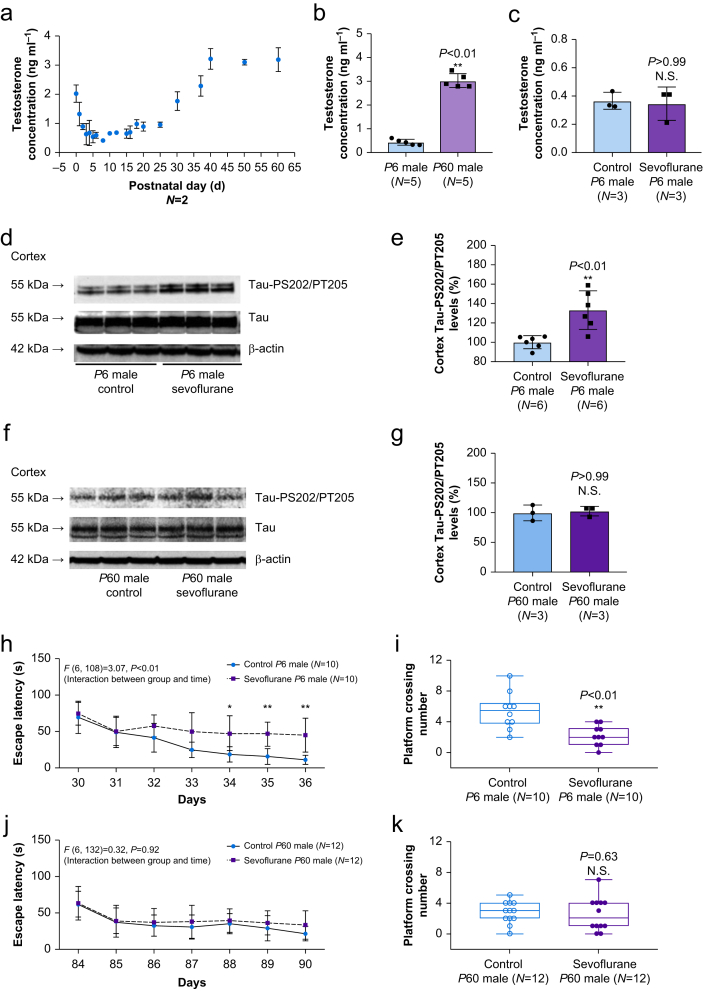
Fig 1.
Differences between neonatal and adult male mice in brain testosterone concentrations, tau phosphorylation, and cognitive function after sevoflurane anaesthesia. (a) Concentrations of testosterone in brain of neonatal and adult mice (n=2 mice per group per day). (b) Brain concentrations of testosterone in P6 and P60 male mice (n=5 mice per group). (c) Effect of sevoflurane on brain testosterone concentrations in P6 male mice (n=3 mice per group). (d) Western immunoblot showing the effects of sevoflurane on the amounts of tau and tau-phospho-Ser202/Thr205 in the cerebral cortex of P6 male mice. (e) Quantification of western immunoblots in P6 male mice (n=6 mice per group). (f) Western immunoblot showing effects of sevoflurane on the amounts of tau and phosph-tau-Ser202/Thr205 in cerebral cortex of P60 male mice. (g) Quantification of western immunoblots in P60 male mice (n=3 mice per group). Effects of sevoflurane on escape latency and platform crossing number in the Morris water maze test in (h and i) neonatal male mice (n=10 mice per group) and (j and k) adult male mice (n=12 mice per group). Student's t-test was used to analyse difference in (b) and (e). Mann–Whitney U-test was used to analyse difference in (c), (g), (i), and (k). The overall P-values in (h and j) refer to interaction of group (control vs sevoflurane) and day (Days 30–36 or Days 84–90) in two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance. Day-specific post hoc P-values are Bonferroni corrected for multiple comparisons. Boxes in (i) and (k) indicate median and inter-quartile range; upper and lower bars indicate minimum and maximum. ∗P<0.05; ∗∗P<0.01. Error bars indicate standard deviation. MWM, Morris water maze; P, postnatal; PS, phosphorylated serine; PT, phosphorylated threonine; N.S., not significant.