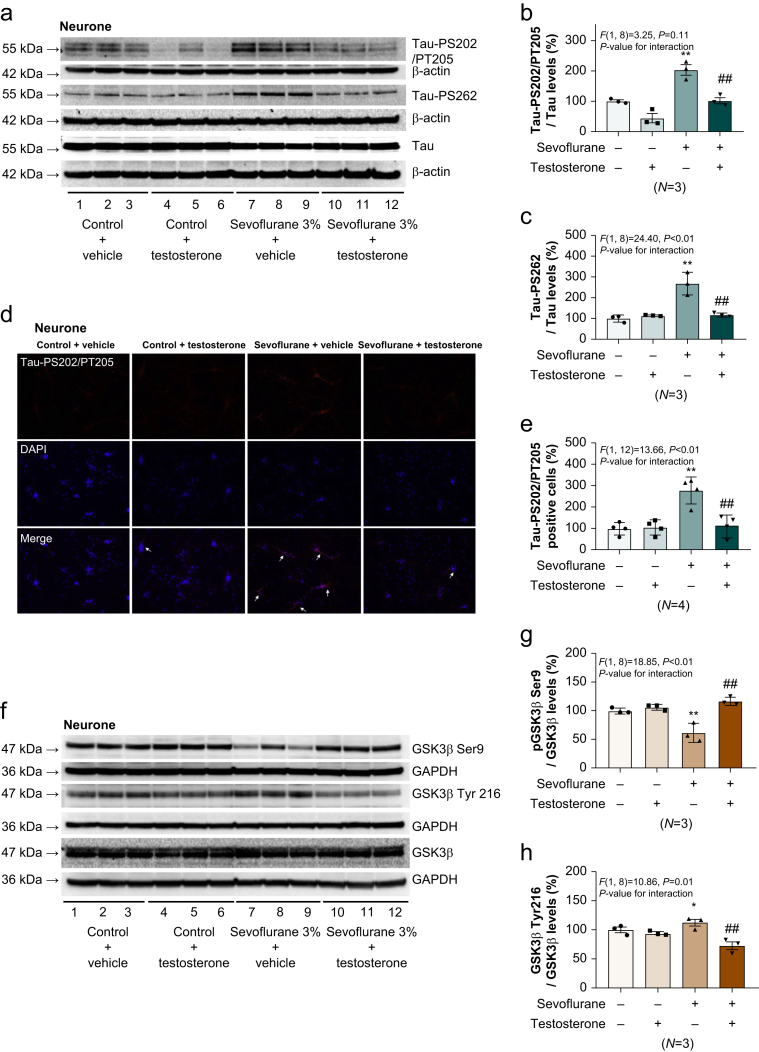
Fig 4.
Testosterone attenuates sevoflurane-induced tau phosphorylation and activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) in primary neurones. (a) Effects of sevoflurane, testosterone, and sevoflurane plus testosterone on the amounts of tau, phospho-tau-Ser202/Thr205, and phospho-tau-Ser262 in primary neurones. Quantification of the ratio of (b) phospho-tau-Ser202/Thr205 to total tau and (c) phospho-tau-Ser262 to total tau (n=3 biological samples per group). (d) Immunohistochemistry imaging showing phospho-tau-Ser202/Thr205-positive primary neurones after treatment with sevoflurane, testosterone, and sevoflurane plus testosterone. (e) Quantification of the immunohistochemistry imaging (n=4 biological samples per group). (f) Effects of sevoflurane, testosterone, and sevoflurane plus testosterone on the amounts of GSK3β, phospho-GSK3β Ser9, and phospho-GSK3β Tyr216 in primary neurones. Quantification of (g) the ratio of phospho-GSK3β Ser9 to total GSK3β and (h) the ratio of phospho-GSK3β Tyr216 to total GSK3β (n=3 biological samples per group). Two-way analysis of variance was used to analyse differences in (b), (c), (e), (g), and (h). ∗P<0.05; ∗∗ and ##P<0.01. Error bars indicate standard deviation. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PS, phosphorylated serine; PT, phosphorylated threonine; Ser9, serine 9; Tyr216, tyrosine 216.