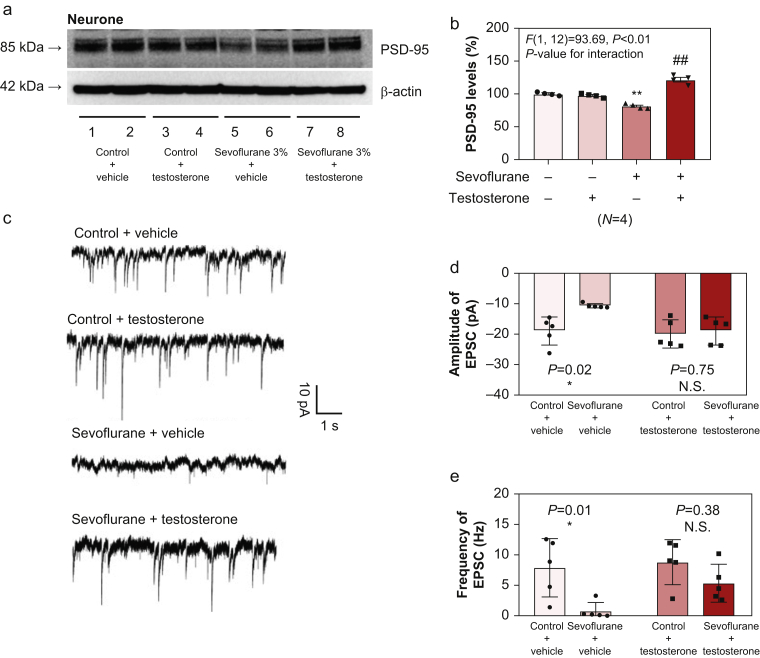
Fig 5.
Testosterone attenuates sevoflurane-induced reduction in postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) and spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) in primary neurones. (a) Effects of sevoflurane and testosterone on the amounts of PSD-95 in primary neurones. (b) Quantification of the western immunoblots of the effects of sevoflurane and testosterone on the amounts of PSD-95 in primary neurones (n=4 biological samples per group). (c) Representative whole-cell current traces showing the effects of sevoflurane and sevoflurane plus testosterone on sEPSCs in primary neurones. Quantification of the effects of sevoflurane and sevoflurane plus testosterone on the (d) amplitude and (e) frequency of sEPSCs in primary neurones (n=5 biological samples per group). Two-way analysis of variance was used to analyse the differences amongst different groups in (b). Unequal variance Student's t-test was used to analyse the difference in different groups in (d) and (e). ∗ and #P<0.05; ∗∗∗ and ##P<0.01. Error bars indicate standard deviation; N.S., not significant.