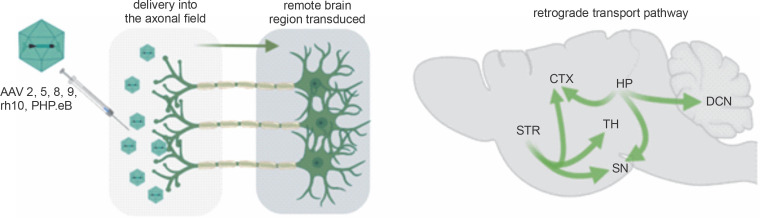
Fig. 1.
Retrograde capabilities of AAV vectors. After delivery of the AAV vector into the axonal field in the CNS, axonal retrograde transport occurs, resulting in transgene expression along the axon, neuronal bodies, and dendrites. The advantage of a single injection of AAV into axonal terminals is that it often results in the transduction of even remote brain structures. Natural properties of the brain’s neuronal networks allow for simultaneous retrograde delivery of AAV encoding transgenes to many brain regions, which is vital for effective gene therapies. (CTX – cortex, DCN – deep cerebellar nuclei, HP – hippocampus, SN – substantia nigra, STR – striatum, TH – thalamus)