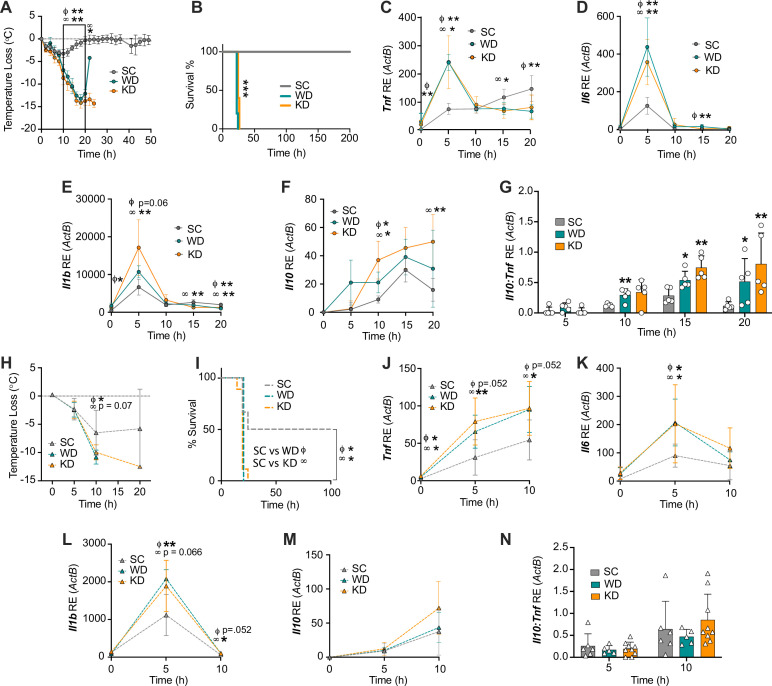
Figure 1. Diets enriched in saturated fatty acids lead to enhanced endotoxemia severity and altered systemic inflammatory profiles, independent of diet-associated microbiome.
(A–G) Age-matched (6–8 weeks) female BALB/c mice were fed standard chow (SC), Western diet (WD), or ketogenic diet (KD) for 2 weeks and injected intraperitoneal (i.p.) with 6 mg/kg of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (A) Temperature loss and (B) survival were monitored every 2 hr. At indicated times, 10–20 μL of blood was drawn via the tail vein, RNA was collected, and samples were assessed for expression of (C) Tnf, (D) Il6, (E) Il1b, and (F) Il10 via qRT-PCR. (G) Il10:Tnf ratio was calculated for 5, 10, 15, and 20 hr post-injection (p.i.) with LPS. (H–N) Next, 19–23-week-old female and 14–23-week-old male and female germ-free C57BL/6 mice were fed SC, WD, or KD for 2 weeks and injected i.p. with 50 mg/kg of LPS. (H) Temperature loss and (I) survival were monitored every 5 hr p.i. (J–N) At indicated times, 10–20 μL of blood was drawn via the tail vein, RNA was collected, and samples were assessed for expression of (J) Tnf, (K) Il6, (L) Il1b, and (M) Il10 via qRT-PCR. (N) Il10:Tnf ratio was calculated for 5 and 10 hr p.i. with LPS. For (A–G), all experiments were run three times, and data are representative of one experiment, n=5 per diet group. For (H–N) SC, n=6; WD, n=5; and KD, n=9; and data are representative of one experiment. For (A, C–G, H, and J–N) a Mann Whitney test was used for pairwise comparisons. For (B) and (I) a log-rank Mantel-Cox test was used for survival curve comparison. For all panels, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. For (C–E), Φ symbols indicate WD significance, and ∞ symbols indicate KD significance. Error bars shown mean ± SD.