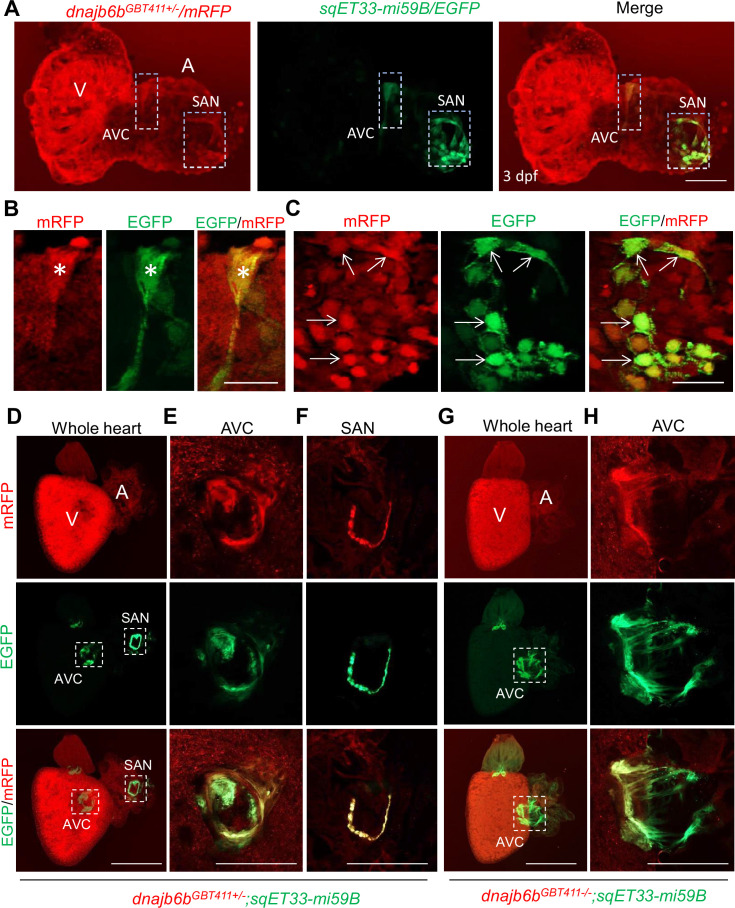
Figure 2. Expression and localization of Dnajb6b in zebrafish cardiac conduction system.
(A–C) Co-localization analysis of mRFP in GBT411/dnajb6b heterozygous mutant with the reporter line sqET33-mi59B in which EGFP labels cardiac conduction system (CCS) in zebrafish embryos. The mRFP reporter for the GBT411 tagged Dnajb6b protein partially overlaps with the EGFP reporter in the sqET33-mi59B transgenic line that labels atrio-ventricular canal (AVC) and sinoatrial node (SAN) in embryonic atrium at 3 dpf. Shown in (B) and (C) are higher magnification images of AVC and SAN in (A), respectively. Stars indicate EGFP + cells in the AVC, and arrows indicate EGFP + cells in the SAN. A: atrium. V: ventricle. dpf, days post-fertilization. (D–H) Co-localization analysis of EGFP in the sqET33-mi59B reporter line after crossed into the GBT411/dnajb6b heterozygous mutants (dnajb6bGBT411+/-;sqET33-mi59B) versus GBT411/dnajb6b homozygous mutants (dnajb6bGBT411-/-;sqET33-mi59B) in adult hearts. In the dnajb6bGBT411+/-;sqET33-mi59B, EGFP is mostly expressed in the AVC within a group of confined cells, and in SAN forming a ring-like structure, which co-localizes well with mRFP. Shown in (E) and (F) are higher magnification images of AVC and SAN in (D), respectively. In the dnajb6bGBT411-/-;sqET33-mi59B, EGFP is mostly detected in the AVC with a more diffused pattern. No ring-like structure with EGFP signal was detected in the SAN. Shown in (H) are higher magnification images of AVC in (G). Scale bars in A, 50 µm; In B, C, 20 µm; In D, G, 500 µm; In E, F, H, 200 µm.