Figure 1.
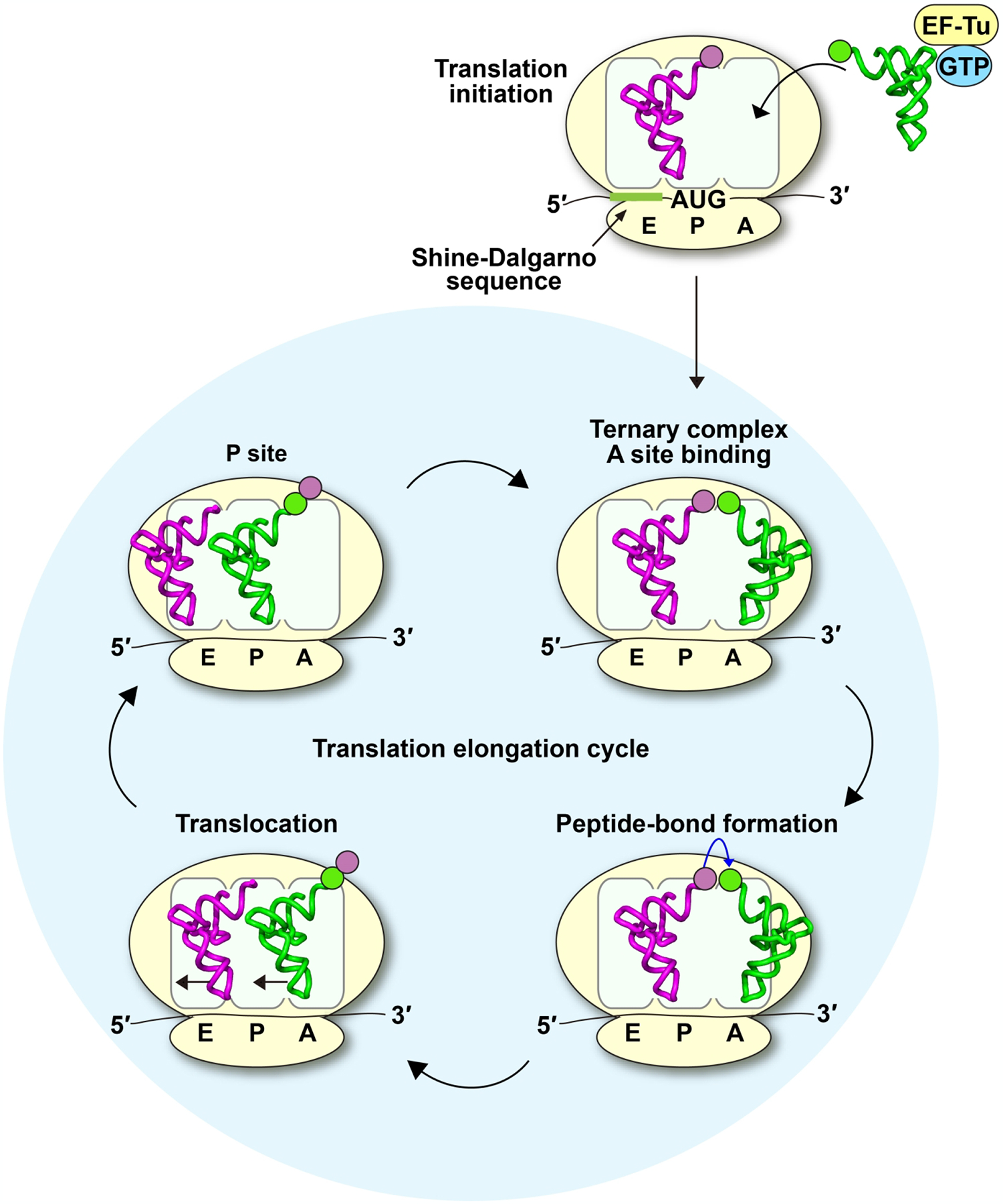
The elongation cycle of protein synthesis in bacteria. A 70SIC is formed with fMet-tRNAfMet sitting on the first AUG codon downstream from the SD sequence of the mRNA. The elongation cycle begins upon delivery of an aa-tRNA to the mRNA codon in the A site via the formation of a TC with EF-Tu and GTP. After the 30S subunit inspects the anticodon-codon pairing in the A site, GTP is hydrolyzed and the aa-tRNA is accommodated. The aminoacyl moiety of the aa-tRNA in the A site accepts the fMet moiety from the P site in a reaction catalyzed by the 50S subunit, forming the dipeptidyl-PRE complex. Subsequently, EF-G-GTP catalyzes translocation of the dipeptidyl-PRE complex into the dipeptidyl-POST complex, positioning the dipeptidyl-tRNA in the P site. A new mRNA codon enters the A site, allowing the elongation cycle to continue until it encounters a stop codon in the A site. Here, tRNAfMet is shown in purple and tRNAPro shown in green, each with the corresponding color of the aminoacyl-group, and the codon.
