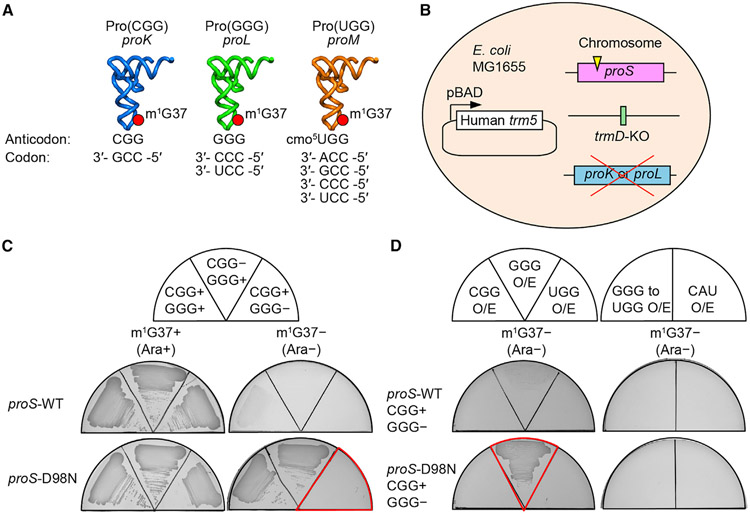
Figure 4. Dependence on Pro(GGG) for survival of proS suppressors.
(A) E. coli proK-encoded Pro(CGG) is responsible for reading the CCG codon; the proL-encoded Pro(GGG) is responsible for reading CC[C/U], and the proM-encoded Pro(UGG) is capable of reading CCN due to the cmo5U34 modification.
(B) Construction of a trmD-KO strain with a proS suppressor in MG1655, followed by deletion of proK or proL.
(C) Depletion analysis of Pro(GGG) or Pro(CGG) of the reconstructed trmD-KO strains expressing proS-WT or proS-D98N.
(D) Isoacceptor complementation analysis of reconstructed trmD-KO strains expressing proS-WT or proS-D98N. O/E, over-expression; GGG to UGG, a variant of Pro(GGG) that changed the GGG anticodon to UGG; CAU, tRNAMet(CAU).