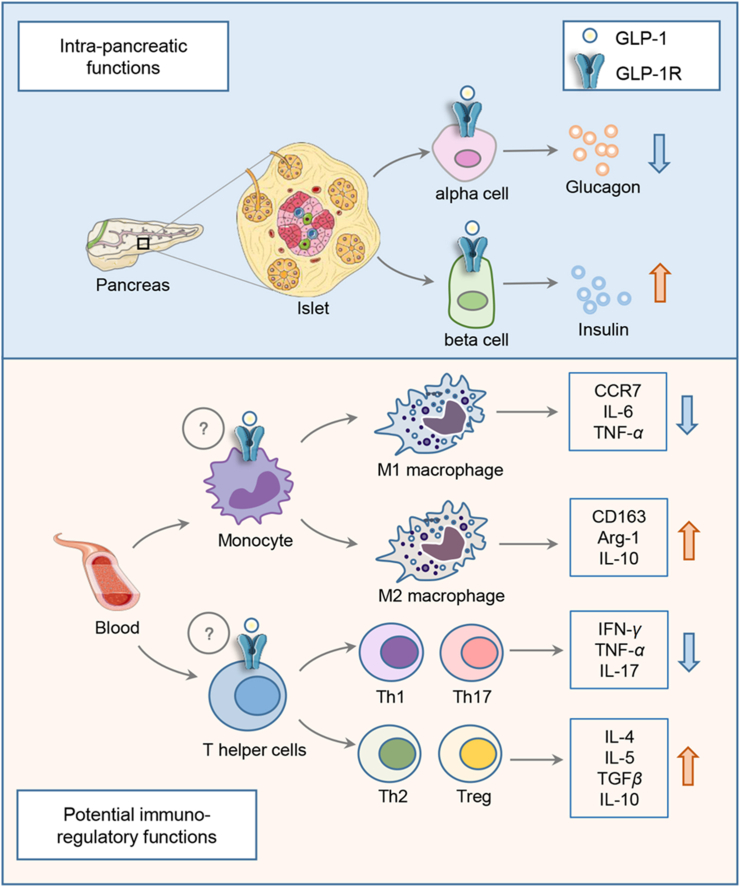
Figure 2.
Illustration of intra-pancreatic and potential immune-regulatory functions of GLP-1RAs. In pancreatic islets, GLP-1 or GLP-1RAs stimulates insulin secretion and represses glucagon secretion by pancreatic β-cells and α-cells, respectively, events that depend on GLP-1R. GLP-1RA in vivo administration exerts its regulatory function in both macrophages and T lymphocytes (T helper cells). It is unclear whether this is mediated by GLP-1R that is expressed in these two cell lineages (indicated with a question mark). In vivo GLP-1RA administration inhibits differentiation of M1 macrophage and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines including CCR7, IL-6 and TNF-α. Conversely, M2 macrophage differentiation and the production of CD163, Arg-1 and IL-10 can be stimulated by in vivo GLP-1RA treatment. Meanwhile, GLP-1RA treatment may inhibit the differentiation of pro-inflammatory T helper cells, including Th1 and Th17, leading to reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interferon γ, TNF-α and IL-17. The differentiation of the anti-inflammatory T helper 2 and regulatory T cells, as well as the production of IL-4, IL-5, TGFβ and IL-10, however, could be promoted by in vivo GLP-1RA treatment.