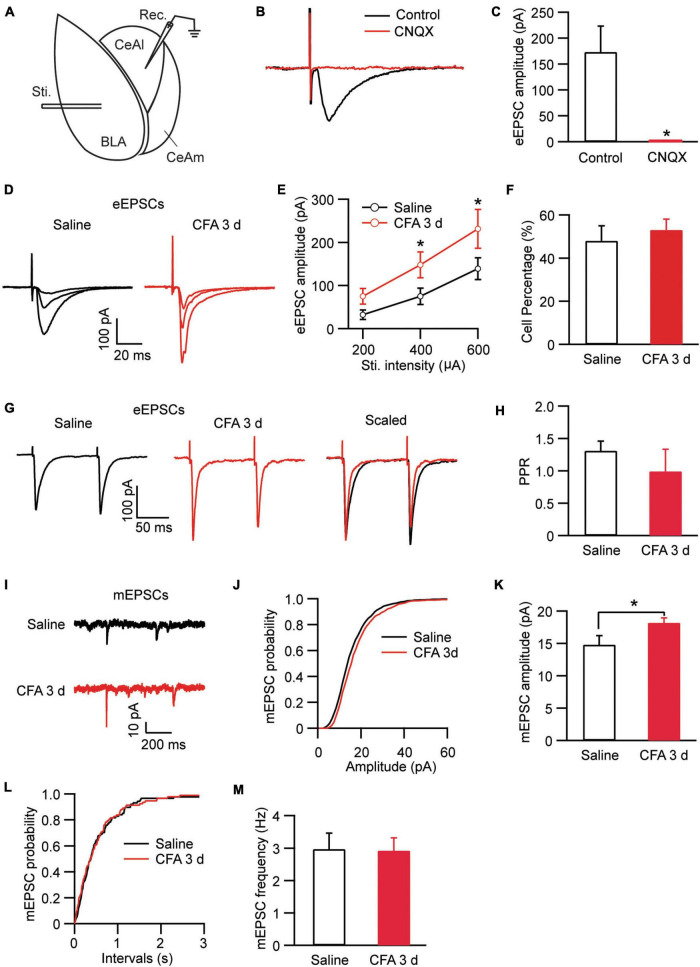
FIGURE 2.
Persistent pain activates the BLA–CeAl pathway. (A) A schematic of recording configuration in amygdala with electrical stimulation (Sti.) in BLA and whole-cell recording (Rec.) in CeAl. (B,C) Sample traces (B) and group data (C) of evoked EPSCs (eEPSCs) in CeAl neurons before (control) and after application of CNQX (10 μM), n = 7. (D,E) Representative traces (D) and group data (E) of eEPSCs evoked by various stimulation intensities in the saline- and CFA-injected rats (n = 9–16 per group). (F) Percentage of CeAl cells displaying BLA-elicited eEPSCs in the saline and CFA groups. (G,H) Current traces (G) and group data (H) of eEPSC pairs evoked by two electrical stimuli (400 μA, 100 ms interval) in the two rat groups. (I–M) Representative traces of miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs, I), group data of mEPSC amplitude (J,K) and mEPSC frequency (L,M) in the saline and CFA groups. *p < 0.05.