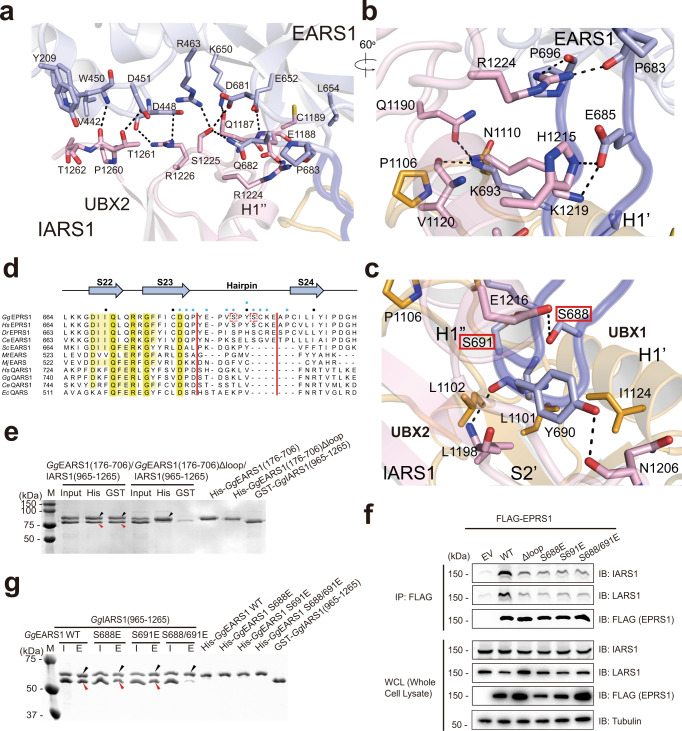
Fig. 2. Interaction between the EARS1 hairpin loop and IARS1 UBX domains.
a Close-up view of the interface between EARS1 and IARS1 UBX2. b, c Close-up view of the interaction between the EARS1 hairpin loop and IARS1 UBX domains. Mutated residues in the pull-down analysis are indicated by red boxes. a–c Color schemes are same as those in Fig. 1d. H-bonds and ion-pairs are shown in black dots. d Structure-based sequence alignments of EARS1 and QARS1 orthologs. The secondary structure of GgEARS1 is displayed on top of the sequences. IARS1-contacting residues are indicated by blue circles. Every tenth residue is marked with a black dot. e In vitro pull-down assay of GgEARS1 and the IARS1 UNE-I domain. His-GgEARS1 or His-GgEARS1Δhairpin was pulled down with Ni-NTA resin, and co-precipitated GST-GgIARS1 was detected by Coomassie staining. Black and red arrowheads indicate eluted His-GgEARS1 and GST-GgIARS1, respectively. f Incorporation of EPRS1 phosphomimetic mutants into the MSC. Flag-tagged, full-length EPRS1 wild-type protein and the phosphomimetic (Ser-to-Glu, S-E) mutant were expressed in HEK293T cells by transient transfection. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody, and co-precipitated IARS1 or LARS1 was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-IARS1 or anti-LARS1 antibody. g Wild-type or phosphomimetic mutant His-GgEARS1 was pulled down with Ni-NTA resin, and co-precipitated GST-GgIARS1 was detected by Coomassie staining. Black and red arrowheads indicate eluted His-GgEARS1 and GST-GgIARS1, respectively. e–g The data are representative of three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.