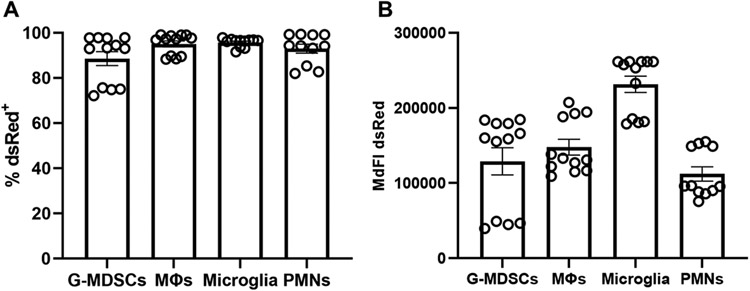
Figure 1. Microglia and leukocytes associated with craniotomy infection readily phagocytose S. aureus in vitro.
Granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs), macrophages (MΦs), microglia, and neutrophils (PMNs) were derived from C57BL/6J mice and challenged with live S. aureus-dsRed at a multiplicity of infection of 10:1 (bacteria:cell). After 2 h, the (A) percentage of dsRed+ cells and (B) median fluorescence intensity (MdFI) was quantified by flow cytometry (n=11-12 biological replicates per cell type combined from three independent experiments).