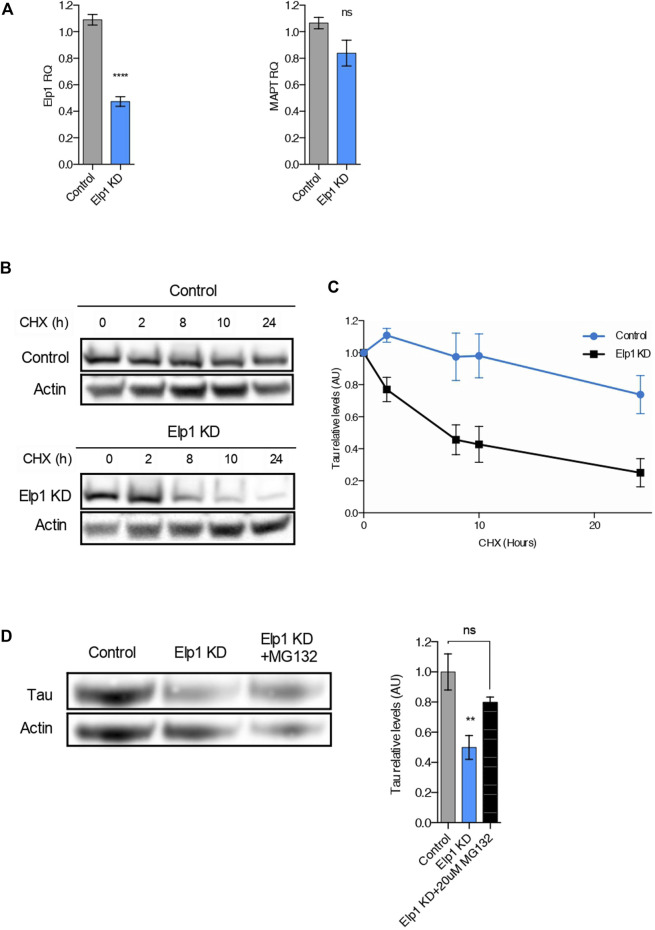
FIGURE 4.
The reduction of Tau levels in ELP1 depletion is due to Tau protein instability. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of Elp1 mRNA (left) and MAPT mRNA (right) in differentiated SHSY5Y extracts from Control and Elp1 KD cells. (B,C) Immunoblotting and quantification of Tau and ß-Actin in differentiated SHSY5Y extracts from Control and Elp1 KD cells incubated with cycloheximide (CHX, 50 μg/ml) for 0, 2, 8, 10 and 24 h. (D) Immunoblotting and histogram of Tau and ß-Actin in differentiated SHSY5Y extracts from Control and Elp1 KD cells incubated with vehicle or MG-132 (20 µM) for 4 h. All graphs show values of means ± SEM. Significance was determined by: (A) two-sided t test, Specifically, [(a left) p < 0.0001; (a right) p = 0.1349; ] (C) two-sided two-way ANOVA. Specifically, [p = 0.0224, F Interaction (4, 44) = 3.173] (D) two-sided one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Specifically, [p = 0.0084, F = 8.5; ] In addition, the post hoc multiple comparisons, to analyze statistical difference of each condition compared to control by Dunnett test, **p < 0.01. n = Number of experimental repeats: (A) Control n = 5; Elp1 KD n = 5; (C) Control n = 5; Elp1 KD n = 7; (D) Control n = 4; Elp1 KD n = 5; Elp1 KD + MG132 n = 3.