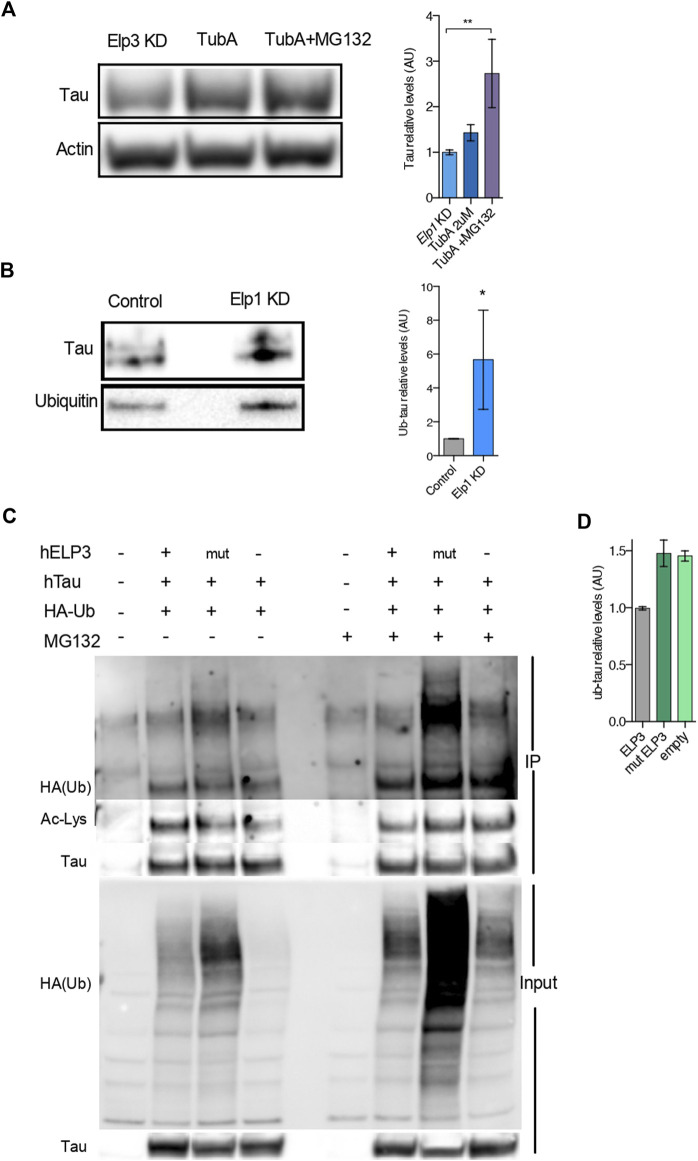
FIGURE 6.
Elongator Deficiency Reduces Tau acetylation, Increases Tau ubiquitylation and induces its Degradation. (A) Immunoblotting and quantification of Tau and ß-Actin in differentiated SHSY5Y extracts from Control and Elp1 KD cells incubated with vehicle, Tubastatin A (TubA, 2 µM) for 24 h or Tubastatin A (TubA, 2 µM) for 24 h together with MG-132 (MG132 , 20 µM) for the last 4 h. (B) Immunoprecipitation followed by Western blotting to detect and quantify ubiquitylated Tau, in control and Elp1KD cells extracts. Histograms of proportion of ubiquitin expression to Tau. (C–D) Immunoprecipitation of Tau followed by Western blotting to detect and quantify ubiquitylated Tau; Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with plasmids expressing WT Tau, HA-tagged ubiquitin and ELP3 or mutated ELP3 in the KAT domain or empty vector incubated with vehicle or MG-132 (MG132 , 17.5 µM) for 15 h. Immunoprecipitates (IP) and total soluble lysates (Input) were analyzed by western blotting, with either anti-HA or anti-acetylated lysine and anti Tau antibodies. (D) Histograms of proportion of ubiquitin expression to Tau incubated with MG-132 (edit graph add stat maybe quantify HA/Tau). All graphs show values of means ± SEM. Significance was determined by: (A) two-sided Kruskal Wallis one-way ANOVA, specifically, [p = 0.0001, K = 11.8; ] In addition, the post hoc multiple comparisons, to analyze statistical difference of each condition compared to Elp1KD by Dunnett test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (B) two-sided t test, Specifically, [(A) p = 0.0286; ]; n = Number of experimental repeats: (A) Elp1 KD n = 6; Elp1 KD + TubA n = 6; Elp1 KD + TubA MG132 n = 5; (B) Control n = 4; Elp1 KD n = 4.