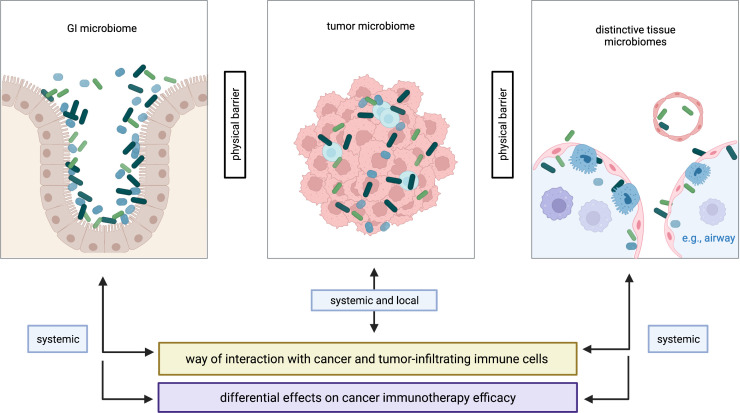
Figure 1.
Compartmentalization of the microbiome in cancer. Distinctive microbiomes are found in various anatomical compartments of patients with cancer, here categorized as GI microbiome, tumor microbiome and distinctive tissue microbiomes. These microbiomes are physically separated yet functionally interact with each other. The tumor microbiota plays an outstanding role as interactions with cancer cells and tumor-infiltrating immune cells may be more direct as compared with the GI microbiome and other tissue microbiomes. Specifically, interactions with tumor and immune cells can occur via the systemic route (eg, circulation) in all three scenarios, while local (‘physical’) interactions are exclusive to the tumor microbiome. This suggests distinct effects of different microbial habitats on cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Figure is created with BioRender.com. GI, gastrointestinal.