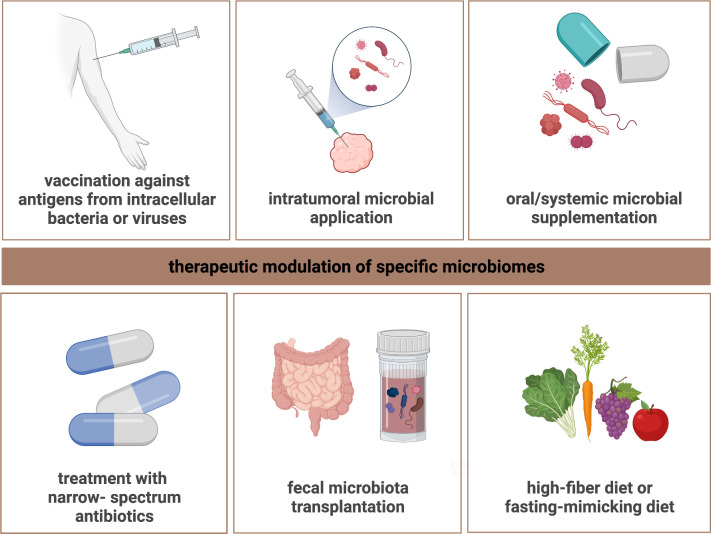
Figure 3.
Concepts for microbiome-centered interventions. Specific microbial compartments may be amenable for therapeutic intervention to resensitize to ICI treatment. Targeted modulation of specific microbiomes may be achieved based on different conceptual approaches. Supplementing particular microbial species (eg, Bifidobacterium) using different routes of administration could modulate the tumor microbiome, the GI microbiome, and the lung microbiome, respectively, to increase the diversity and/or make the functional composition more beneficial. On the other hand, the use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics against harmful bacteria or FMT from ICI-responding patients could restore ICI efficacy in otherwise non-responding/refractory patients. Personalized vaccination against tumor-associated antigens from intracellular bacteria or viruses represents another strategy by which microbial species might be harnessed for ICI-resensitizing intervention. Finally, adopting specific dietary behaviors such as high-fiber- or fasting-mimicking diet may also facilitate ICI performance by inducing favorable immunological changes in the TME. Figure is created with BioRender.com. FMT, fecal microbiota transplantation; GI, gastrointestinal; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; TME, tumor microenvironment.