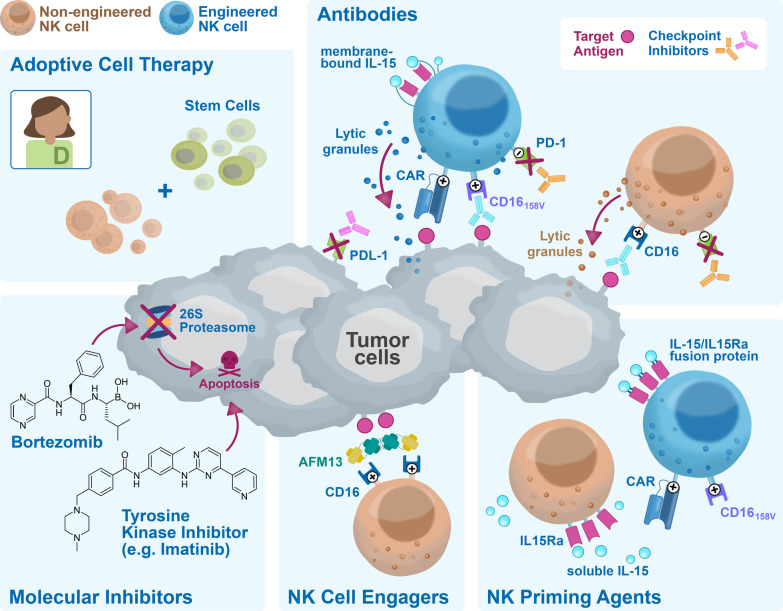
Fig. 6.
Overview of combination non-engineered and engineered NK cell therapies. From top left: in combination with adoptive cell therapy, NK cells are administered with stem cells from a healthy donor. Monoclonal antibodies are combined with NK cells to enhance tumor targeting via antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) through endogenous CD16 or engineered high-affinity non-cleavable hnCD16 (158 V) on NK cell surface, or as checkpoint inhibitors to block inhibitory receptors on the surface of NK cells (such as programmed cell death protein 1, PD-1) or to block inhibitory ligands on the surface of target cancer cells (such as programmed death-ligand 1, PD-L1). NK cell priming agents, such as IL-15 or IL-15 and IL-15 receptor fusion protein IL-15/IL-15Ra, stimulate NK activation in vivo. NK cell engagers (NKCE) are synthetic molecules built from fragments of monoclonal antibodies engaging simultaneously a tumor-associated antigen (TAA) on the cancer cells and CD16 on the NK cells (e.g., AFM13). Molecular inhibitors act on target cancer cells, inducing apoptosis via inhibition of the proteasome (Bortezomib) or via inhibition of tyrosine kinases (e.g., Imatinib)