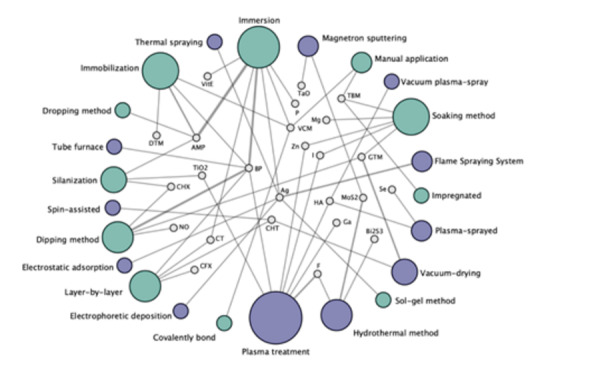
Figure 3. The network analysis about the most common functional compounds incorporated onto Ti surface using different deposition methods in preclinical studies. Green nodes represent the chemical deposition methods and purple nodes the physical deposition methods. The size of the node is proportional to the number of animal studies included. Gray lines represent the direct comparisons of each antimicrobial deposition method, and the line thickness is directly proportional to the number of incorporations. [ Abbreviations: AMP = antimicrobial peptides; BP = biopolymers; VitE = Vitamin E; DTM = Daptomycin; CHX = Chlorhexidine; NO = nitric oxide; CT = catechol; CFX = Ciprofloxacin; CHT = Chitosan; F = Fluoride ion; Ga = Gallium ion; HA = Hydroxyapatite; MoS2 = Molybdenum disulfide; Bi2S3 = Bismuth sulfide; Se = Sellenium ion; GTM = Gentamycin; TBM = Tobramycin; TaO = Tantalum oxide; P = Red Phosphorus; VCM = Vancomycin; Zn = Zinc ion; I = Iodine ion; Ag = Silver ion; and TiO2 = Titanium dioxide]. Reprinted from Costa et al. 2021 [27]; Copyright (2021); with permission from Elsevier (License number: 5214900523221).