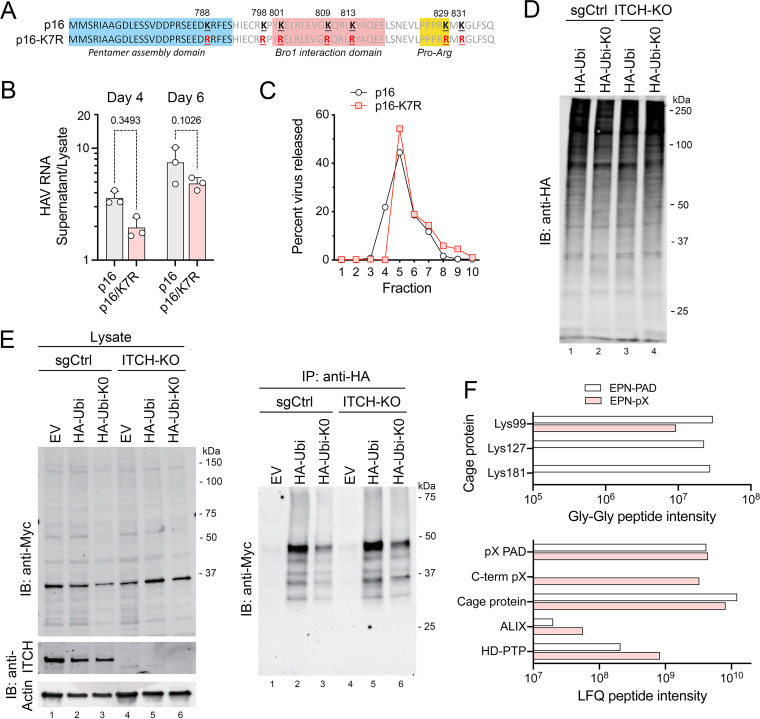
FIG 6.
Protein ubiquitylation and eHAV release. (A) pX sequence in p16 and mutant p16-K7R virus with Arg substitutions of all 7 pX Lys residues. (B) Extracellular release of p16-K7R virus relative to the parent p16 virus, calculated from the ratio of HAV RNA in extracellular fluids versus cell lysate generated by each viral RNA at 4 and 6 days posttransfection. P values were calculated by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple-comparison test. (C) Percentage of extracellular HAV RNA banding in fractions of isopycnic minigradients loaded with supernatant fluids from cells transfected 5 days previously with p16 or p16-K7R genomic RNA. Extracellular p16-K7R virus bands at the same density as eHAV. (D) Immunoblot showing global protein ubiquitylation in ITCH-KO and control (sgCtrl) cells transfected with EPN-pX and vectors expressing either HA-tagged ubiquitin (HA-Ubi) or an HA-ubiquitin mutant lacking Lys residues (HA-Ubi-K0). Cells were treated with MG132 for 2 h prior to harvest. (E) EPN-pX ubiquitylation in cells transfected with HA-Ubi, HA-Ubi-KO, or empty vector (EV). Immunoblots show EPN-pX (Myc, ~33 kDa) and ITCH in cell lysates (left) and EPN-pX in anti-HA precipitates (right). (F, Top) Normalized intensities of nanocage protein peptides with Gly-Gly ubiquitin remnants identified in the EPN-pX and EPN-PAD proteomics samples. (F, Bottom) Normalized LFQ intensities of all peptides from selected proteins present in EPN-pX and EPN-PAD samples. C-term pX, C-terminal sequence unique to EPN-pX and not present in EPN-PAD.