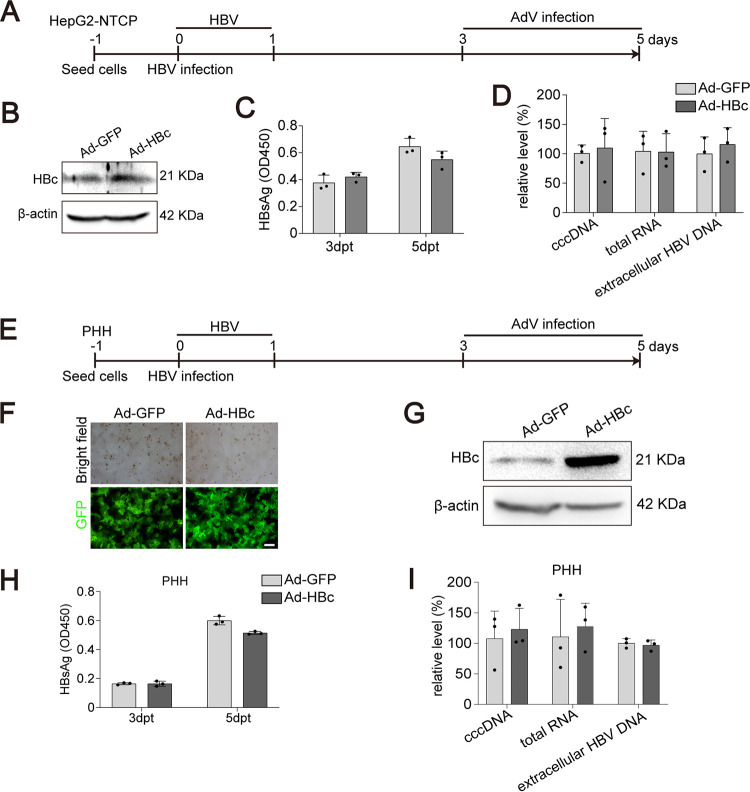
FIG 4.
Effect of HBc overexpression in HBV infection models. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental setting. HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with HBV (MOI = 100). Three days postinfection, the cells were transduced with AdV (MOI = 1) for 48 h. The culture supernatants were collected at 3 days and 5 days postinfection. (B) The expression of HBc was evaluated by Western blotting. (C) The level of extracellular HBsAg was measured by ELISA. (D) The relative levels of intracellular HBV RNA, HBV cccDNA, and extracellular HBV DNA were determined by qPCR. (E) Schematic representation of the experimental setting. PHHs were infected with HBV (MOI = 100). Three days postinfection, the cells were transduced with AdV (MOI = 1) for 48 h. The culture supernatants were collected at 3 days and 5 days postinfection. (F) Transduction efficiency of adenovirus was evaluated by fluorescence intensity of GFP. Bar, 50 μm. (G) The expression of HBc in adenovirus-transduced cells was detected by Western blotting. (H) The level of secreted HBsAg was evaluated by ELISA. (I) Intracellular HBV RNA, HBV cccDNA, and extracellular HBV DNA were measured by qPCR. Data were presented as mean ± SD.