FIGURE 1.
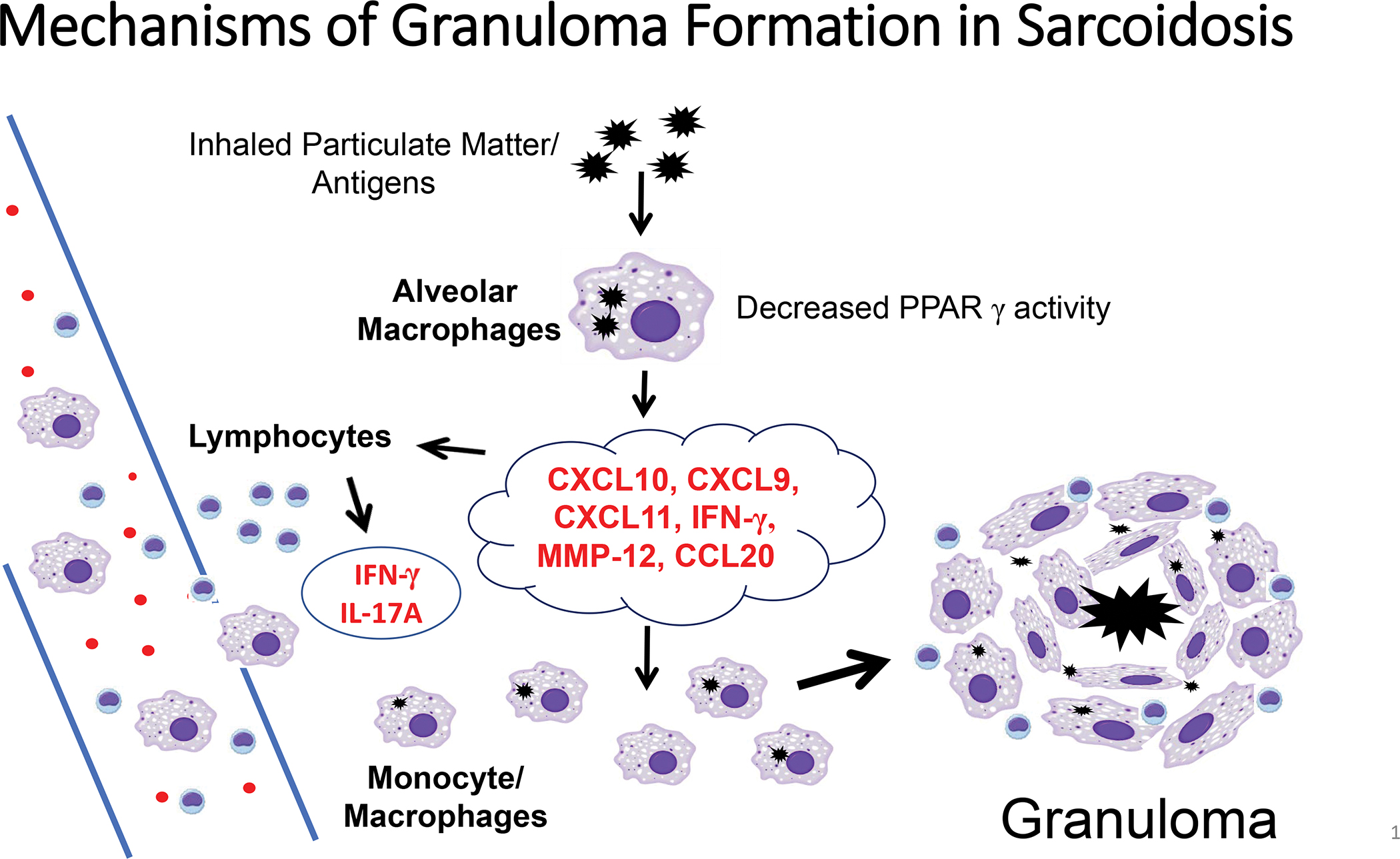
The pathophysiology of sarcoidosis granuloma formation begins when alveolar macrophages contact inhaled particulate matter that is antigenic and capable of initiating immune activation of macrophages, dendritic cells and lymphocytes. Lymphocytes and macrophages generate products (chemokines CXCL9, CSCL10, CSCL11, CCL20; cytokines IFN-γ, IL-17A; enzymes MMP-12) that organize macrophages into giant cells and granuloma structures.
