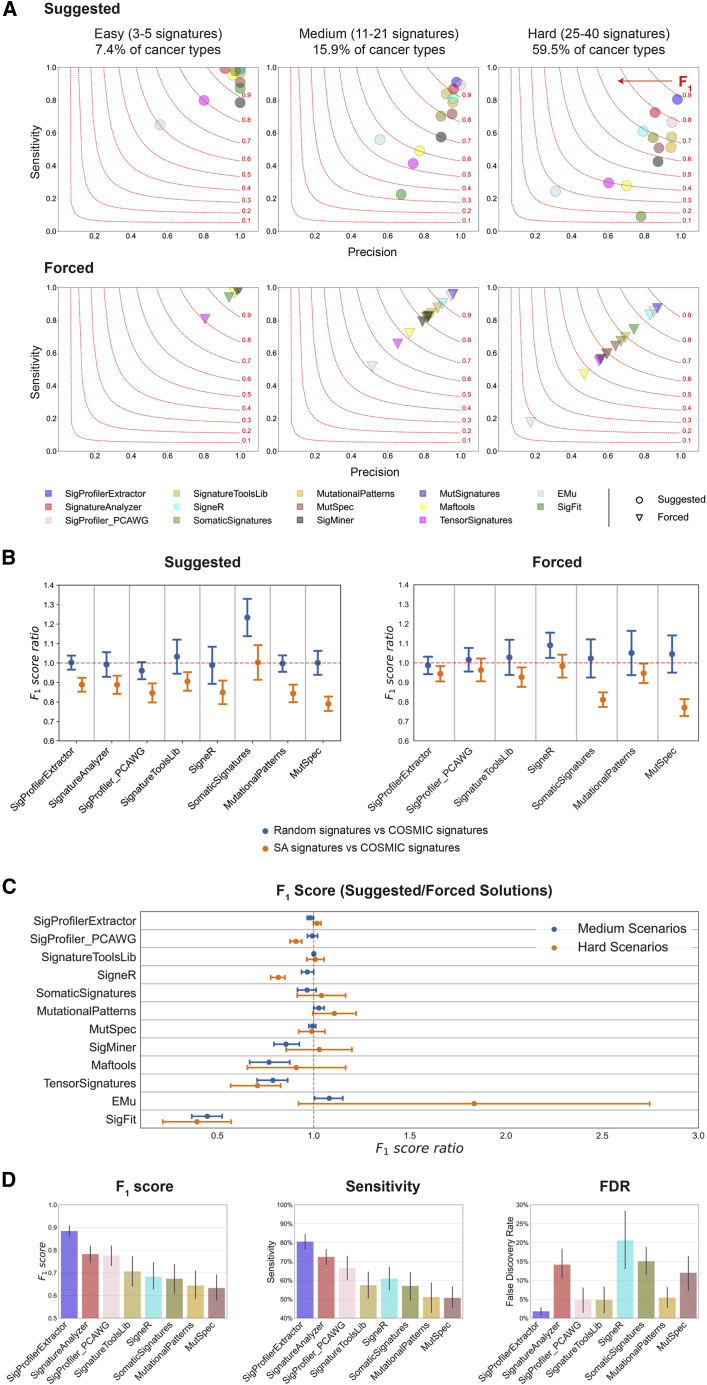
Figure 2.
Benchmarking of bioinformatics tools for de novo extraction of mutational signatures using SBS-96 noiseless scenarios
(A) Average precision (x axes), sensitivities (y axes), and F1 scores (harmonic mean of precision and sensitivity; red curves) are shown across the three types of scenarios. Different tools are displayed using circles and triangles with different colors. Circles are used to display results for suggested model selection, which most closely matches analysis of a real dataset. Triangles are used to display results for forced model selection, where tools were required to extract the known total number of ground-truth mutational signatures. All triangles are located on the diagonal, as the forced model selection results in equal numbers of false-positive and false-negative signatures.
(B) Evaluating the effect of ground-truth signatures on the de novo extraction by different tools (x axes). Ratio of F1 scores (y axes) with standard errors of the mean were calculated for medium complexity scenarios simulated using COSMIC, SA, or random signatures. Ratio of approximately 1.00 indicates a similar performance between different types of signatures.
(C) Evaluating the performance of de novo extraction between suggested and forced selection for different tools (x axes). Ratio of F1 scores (y axes) with standard errors of the mean was calculated for all medium and hard scenarios. Ratio of approximately 1.00 indicates a similar performance between suggested and forced model selection.
(D) Summary of the performance for the top eight tools on hard SBS-96 noiseless scenarios with suggested model selection. Vertical axes reflect F1 score (left plot), sensitivity (middle plot), and false discovery rate (right plot), respectively. Error bars correspond to standard errors of the mean.
Results from SignatureAnalyzer and MutSignatures are not displayed in (A)–(C) for forced and suggested model selections, respectively, as the tools do not support these types of analyses.