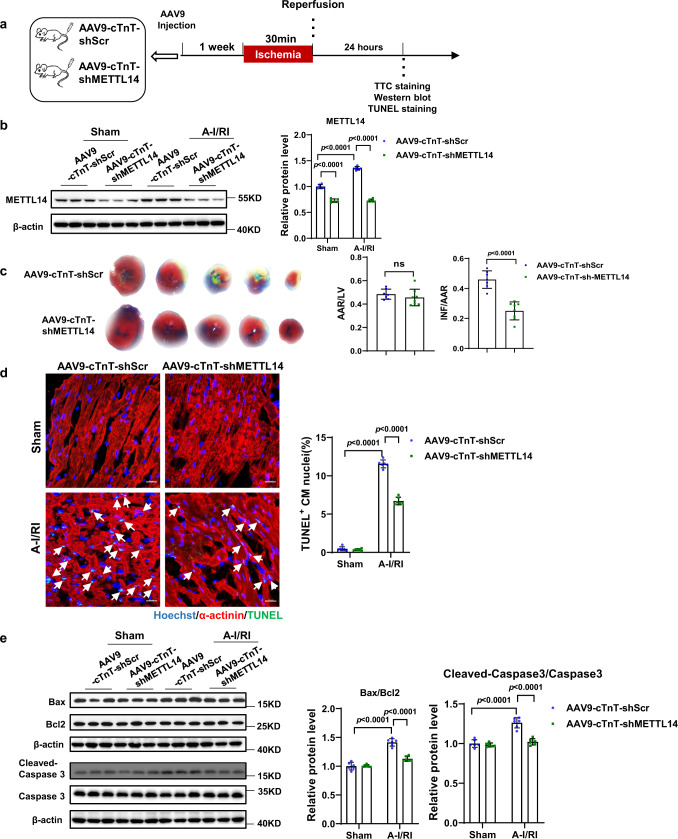
Fig. 5. Cardiac-specific knockdown METTL14 alleviates acute myocardial I/R injury in mouse hearts.
a Schedule of virus injection and acute myocardial I/R injury model establishment. b Representative western blot and statistical data of METTL14 expression levels in mouse hearts treated as indicated (n = 6 mice/group). c Representative images of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining and quantification of the area at risk/left ventricular weight (AAR/LV) ratio and the infarct size/area at risk (INF/AAR) ratio (n = 7 and 8 mice, respectively). d Representative images of immunofluorescence staining and quantification of the TUNEL positive cardiomyocytes in mouse hearts treated as indicated (n = 6 mice/group). Scale bar: 20 μm. e Representative western blot and statistical data of myocardium apoptosis by detection of Bax, Bcl2, caspase 3, and Cleaved-Caspase 3 expression levels in mouse hearts treated as indicated (n = 6 mice/group). AAV9-cTnT-shScr, cardiac-specific troponin-T promoter-driven Scramble AAV9; AAV9-cTnT-shMETTL14, cardiac-specific troponin-T promoter-driven METTL14 knockdown AAV9; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; ns, nonstatistically significant; I/R, ischemia-reperfusion. All data are expressed as means ± SD. b, d, and e, two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test; c, independent-sample t-test, two-sided. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.