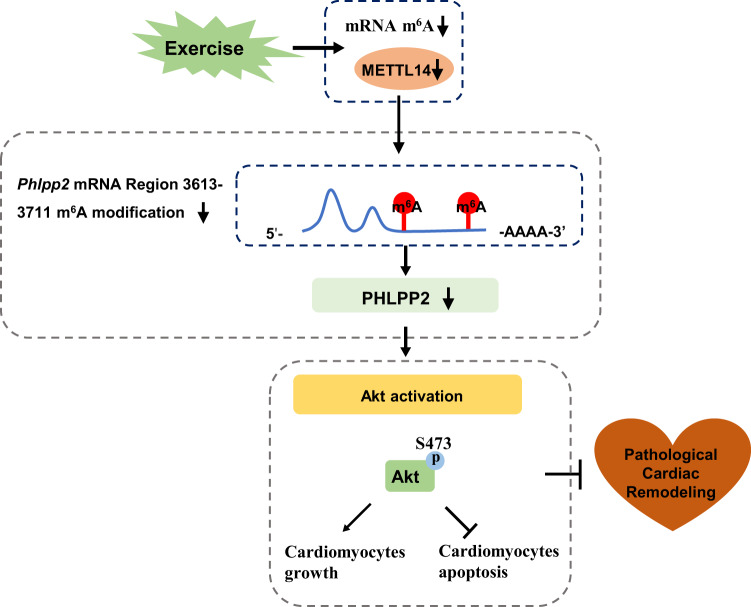
Fig. 9. Proposed working model by which downregulation of RNA m6A methyltransferase METTL14 contributes to exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy and protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Endurance exercise leads to a reduced mRNA m6A methylation level. Cardiac-specific knockdown METTL14 reduces global RNA m6A modification, thereby attenuating acute I/R injury as well as cardiac dysfunction in I/R remodeling. Mechanistically, silencing METTL14 regulates Phlpp2 mRNA (ranging nucleotides 3613–3711 in Rattus) m6A modification and activates Akt-S473 which regulates cardiomyocyte growth and apoptosis.