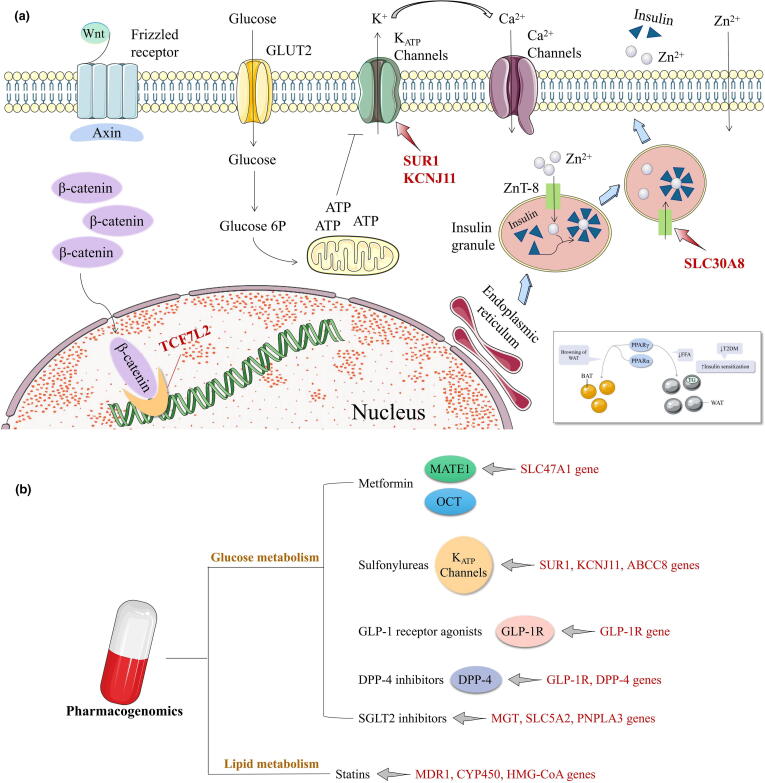
Fig. 1.
Genetic variants associated with glycolipid metabolic disorders. a. Overview of canonical signaling mechanisms involved in beta-cell glucose sensing and responses to secretory potentiators or inhibitors. TCF7L2 (Transcription factor 7-like 2) has a role in the canonical Wnt (Wingless-type MMTV integration site) pathway. SLC30A8 (Solute-linked carrier 30, member 8) encodes ZnT8 (Zinc transporter 8) which regulates the influx of zinc into intracellular vesicles of insulin is presumed to be critical for insulin storage and secretion. KCNJ11 (K+ inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11) and SUR1 (Sulfonylurea receptor 1) encode KATP channel together, thus indirectly sensing blood glucose concentrations and controlling insulin release. PPARs (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) in glycolipid metabolism disorder. BAT, brown adipose tissue; FFA, free fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; TG, triglycerides; WAT, white adipose tissue. b. Pharmacogenomics and its targets in glycolipid metabolic disorders. MATE1, multidrug and toxin extrusion 1; OCT, organic cation transporters; SLC47A1, solute carrier family 47 member 1; SUR1, Sulfonylurea receptor 1; KCNJ11, K+ inwardly rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 11; ABCC8, ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 8; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; MGT, magnesium transporter; SLC5A2, solute carrier family 5 member 2; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3; MDR1, multidrug resistance gene 1; CYP450, cytochrome P450; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A.