Figure 7.
The loss of sacsin disrupts protein-protein interactions
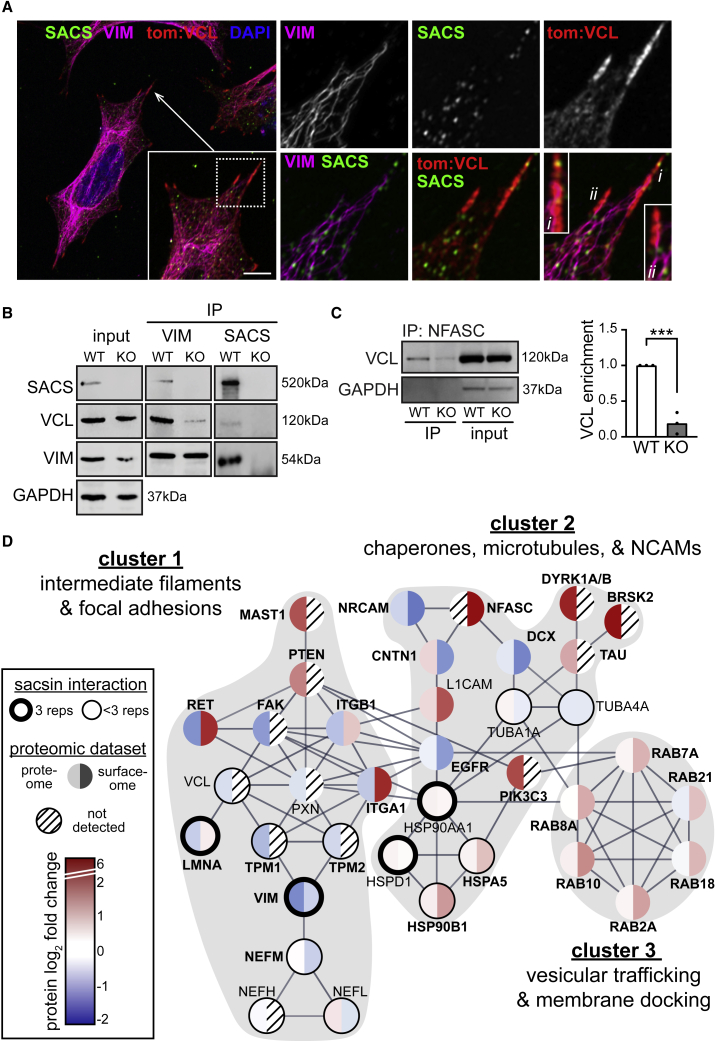
(A) Airyscan confocal analysis of sacsin, vimentin, and transfected tdTomato:vinculin staining in WT SH-SY5Y cells, demonstrating sacsin localization along vimentin tracts and FAs. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(B) Vimentin or sacsin were immunoprecipitated from WT and sacsin KO SH-SY5Y cells, and co-immunoprecipitated proteins (sacsin, vinculin, vimentin) were analyzed by western blot.
(C) Co-IP of NFASC and vinculin in WT and sacsin KO cells shows that the interaction between VCL and NFASC is greatly reduced in sacsin KO cells, despite NFASC being substantially overexpressed in SACS KO cells (Figure 5C). n = 3, SEM, Student’s t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(D) STRING protein interaction map depicting proteins quantified in this study. Lines between proteins indicate high-confidence interactions (interaction score >0.7). We removed proteins with redundant interactions for clarity (for example, most integrins have largely overlapping interactomes). Proteins identified in the sacsin interactome profiling are circled, with the thick circles marking interactors identified in all replicates and the thin circles marking interactors identified in <3 replicates. Proteins are colored by log2 f.c. in proteome (left half) and cell surface proteome (right half). Clusters identified by k-means clustering are marked by gray background.