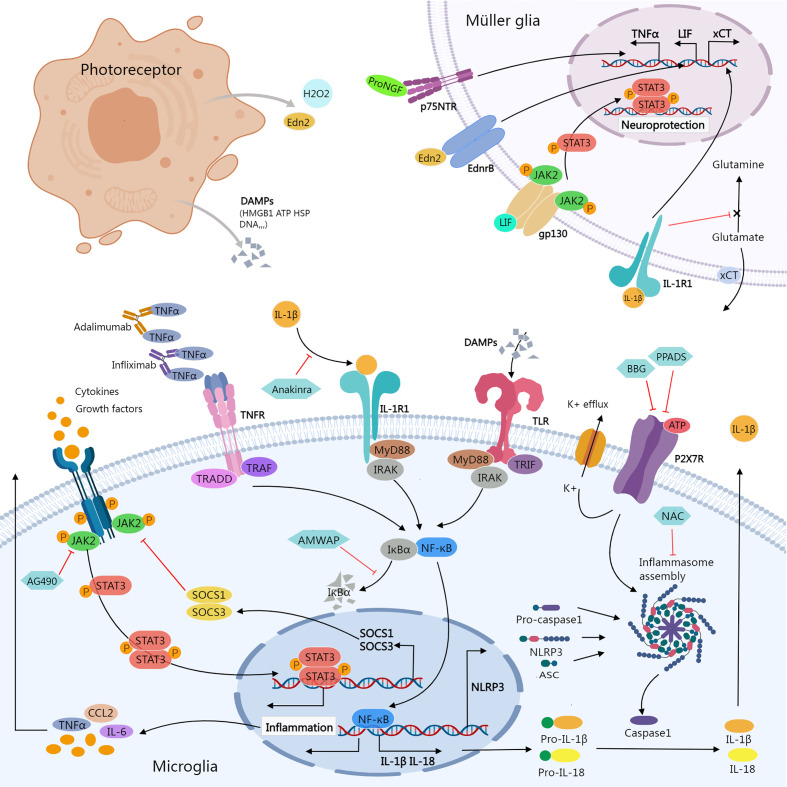
Figure 1.
Inflammatory signals between photoreceptor, microglia, and Müller glia. Damaged or dying photoreceptors release signal molecules that stimulate the activation of microglia and Müller glia. In Müller glia, activation of NFGR promotes TNFα production; Edn2 binds to Ednrb promotes LIF transcription; LIF binding to gp130 activates the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, which promotes Müller glial neuroprotection; IL-1β binding to IL-1R1 interferes with glutamate conversion into glutamine, resulting in elevated extracellular glutamate concentration. In microglia, activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling stimulates the release of inflammatory molecules. SOCS1/SOCS3 act as negative feedback factors of JAK/STAT pathway; AG490 specifically inhibits JAK2. Ligands-binding to TNFR, IL-1R, and TLR stimulates NF-κB signaling cascades, promoting transcription of inflammatory genes including NLRP3, pro-IL-1β, and pro-IL-18; ATP stimulates K+ efflux via P2X7R, promoting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the release of active caspase-1, mature IL-1β, and IL-18. Biological agents like infliximab and adalimumab provide neuroprotection by neutralizing TNFα. Anakinra blocks the biologic activity of IL-1β. AMWAP prevents NF-κB translocating into the nucleus by inhibiting IκBα degradation. NAC suppresses the activation of NLRP3. BBG and PPADS reduce the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome via inhibiting P2X7R signaling. AMWAP, activated microglia/macrophage WAP domain protein; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BBG, Brilliant Blue G; CCL2, C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; Edn2, endothelin 2; Ednrb, endothelin receptor B; HMGB1, High-mobility group box-1; HSP, heat shock protein; JAK, janus kinase; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; PPADS, pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2’,4’-disulfonic acid; proNGF, pro-nerve growth factor; p75NTR, p75 neurotrophin receptor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TNFR, Tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRADD, TNFR1-associated death domain protein; TRAF, TNF receptor associated factor; TLR, Toll-like receptors; TRIF, TIR-domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon-β; xCT, core subunit of the cystine/glutamate transporter system xc-; IRAK, Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase.