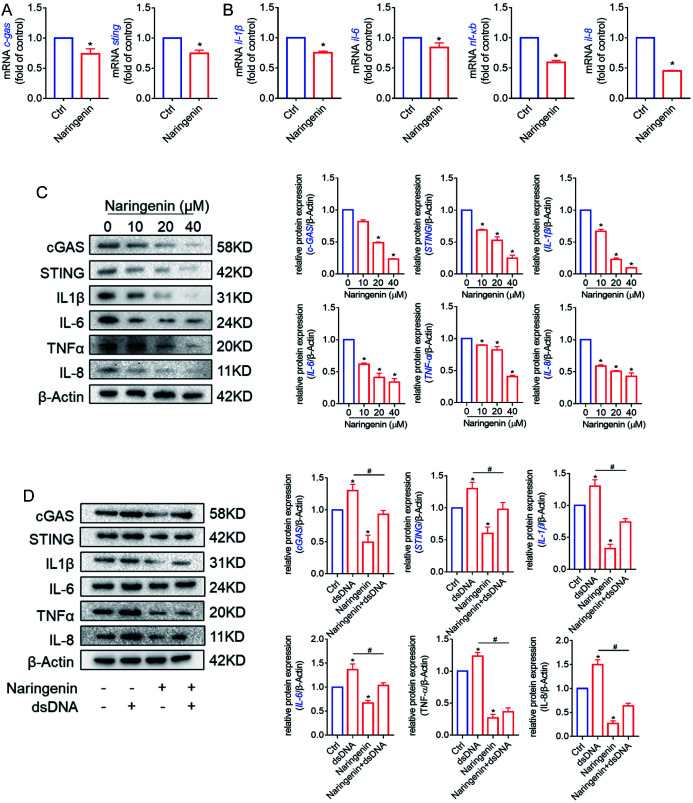
Fig. 6. Naringenin reduces the secretion of inflammatory factors in LX2 cells by inhibiting cGAS pathway.
HSC-LX2 were treated with naringenin for 24 h. (A) Naringenin significantly reduced the mRNA levels of cGAS and STING in LX2 (B) Naringenin inhibited the mRNA expression of inflammatory factors, such as IL-1β, IL-6, NF-kappa B, and IL-8 in LX2 cells. (C) WB assay show that naringenin dose-dependently reduced the protein expression of cGAS, STING, and related inflammatory factors in LX2 cells, quantitative analysis, n=3. *p<0.05, versus naringenin (0 µM). (D) WB assay show that dsDNA promoted the secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-8 by activating cGAS and STING, while naringenin suppressed those effects, quantitative analysis, n=3. *p<0.05, versus control; #p<0.05, versus dsDNA treatment. α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin; cGAS, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase; STING, stimulator of interferon genes.