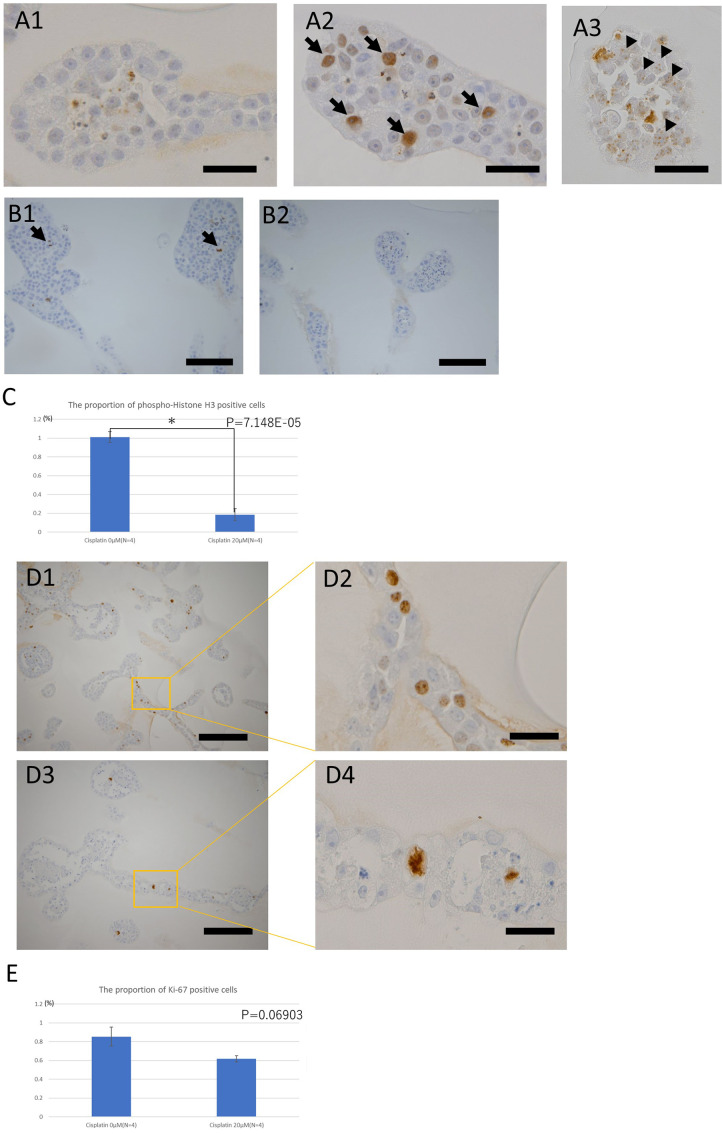
Fig. 4.
Immunohistochemistry studies of the toxic effects of cisplatin on the organoids derived from KS cells.
A: Immunohistochemistry of the DNA damage marker γ-H2AX. Distribution of the sites positive for γ-H2AX under each condition: bar=40 µm. A1: The nuclei of the tubular structures of the organoids not exposed to cisplatin were negative to γ-H2AX. A2: Tubular structure of organoids exposed to 30 µM cisplatin for 24 h. Positive sites for γ-H2AX often had a pan-nuclear distribution (arrows). A3: Tubular structure of organoids exposed to 10 µM cisplatin for 144 h. The positive sites for γ-H2AX had a punctate distribution in the nucleus (arrowheads). B: Immunohistochemistry of the cell division marker, phospho-histone H3. Comparison of the proportions of positive cells for each condition: bar=100 µm. B1: Tubular structures of the organoids not exposed to cisplatin. A few positive cells (dividing cells) (arrows) were observed. B2: Tubular structures of organoids exposed to 30 µM cisplatin for 144 h. No positive cells were observed. C: The proportion of phospho-histone H3-positive cells in organoids exposed or not exposed to 20 μM cisplatin for 144 h. (n=4 for both). Three tissue sections of each organoid at different levels were prepared and five randomly selected fields including the tubular structure were taken in each section. D: Immunohistochemistry of cell proliferation marker Ki-67. Comparison of morphology of positive cell nuclei under each condition. D1: Tubular structures of the organoid not exposed to cisplatin; Bar=200 µm. D2: Magnified image of D1; Bar=40 µm. D3: Tubular structures of the organoid exposed to 10 µM cisplatin for 144 h; Bar=200 µm. D4: Magnified image of D3; Bar= 40 µm. Morphologically abnormal nuclear division was observed in the organoids exposed to cisplatin. E: The proportion of Ki-67-positive cells in organoids exposed, or not exposed, to 20 μM cisplatin for 144 h (n=4 in both groups). Three tissue sections of each organoid at different levels were prepared and five randomly selected fields, including the tubular structure, were taken from each section.