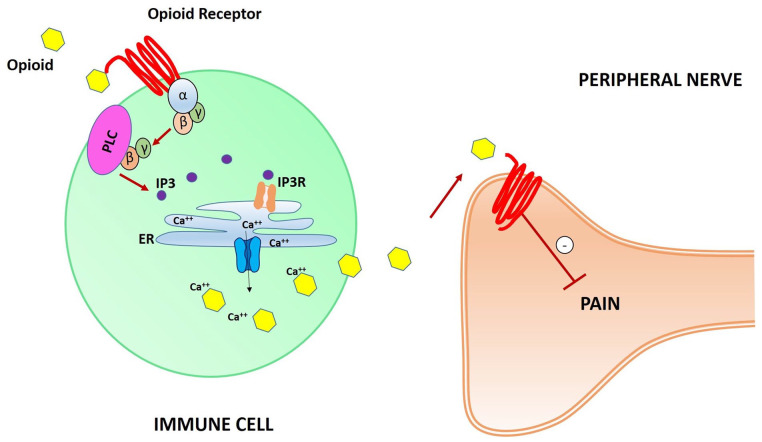
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of opioid receptors on leukocytes’ surface-mediated synaptic pain pathway. Opioid peptides bind opioid receptors, activating Gi proteins. G-βγ subunits activate phospholipase C (PLC), leading to the second inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) messenger production and subsequent IP3 receptor (IP3R) activation in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Ca++ ions are released from the ER, leading to the extracellular delivery of intracellular Ca++-dependent opioid peptides. Thus, opioid receptors on peripheral nerve cell membranes are activated and pain pathways are inhibited.