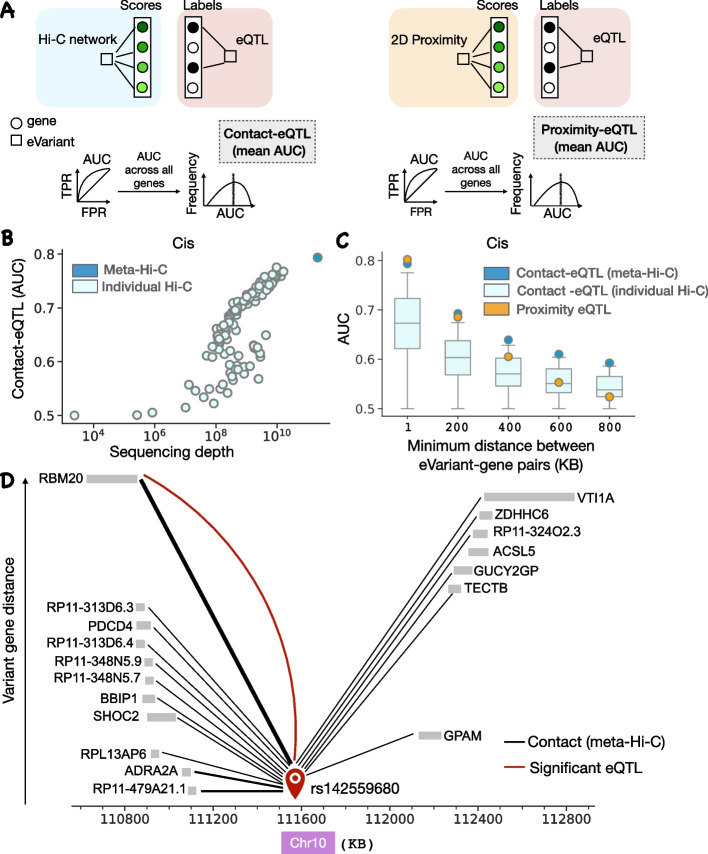
Fig. 3.
Meta-Hi-C network captures long-range eQTLs. A Contact-eQTL and proximity-eQTL metric schematic. For contact-eQTL and proximity-eQTL, for each variant, the edges are ranked by contact frequency or inverse of the genomic distance from the gene respectively. The labels are obtained from eQTL associations (Section Methods). We perform this task for every variant and then report the average AUC across all variants. B Contact-eQTL for individual Hi-C network and meta-Hi-C network at 1-KB resolution as a function of sequencing depth. C The boxplot shows the distribution of contact-eQTL for each project at various minimum distance thresholds. Circles represent the contact-eQTL of the meta-Hi-C network and proximity-eQTL. D An example comparing contact-eQTL with proximity-eQTL. All genes associated with eVariant rs142559680 along with their sequence position on the X axis. The vertical separation between gene and variant increases as the distance between the variant and gene TSS increases. The thickness of the variant gene edge increases with an increase in the contact frequency in the meta-Hi-C network. Although gene RP11-479A21.1 is the closest to the variant, gene RBM20 has the strongest contact with the variant and is also the only significantly associated gene with the variant