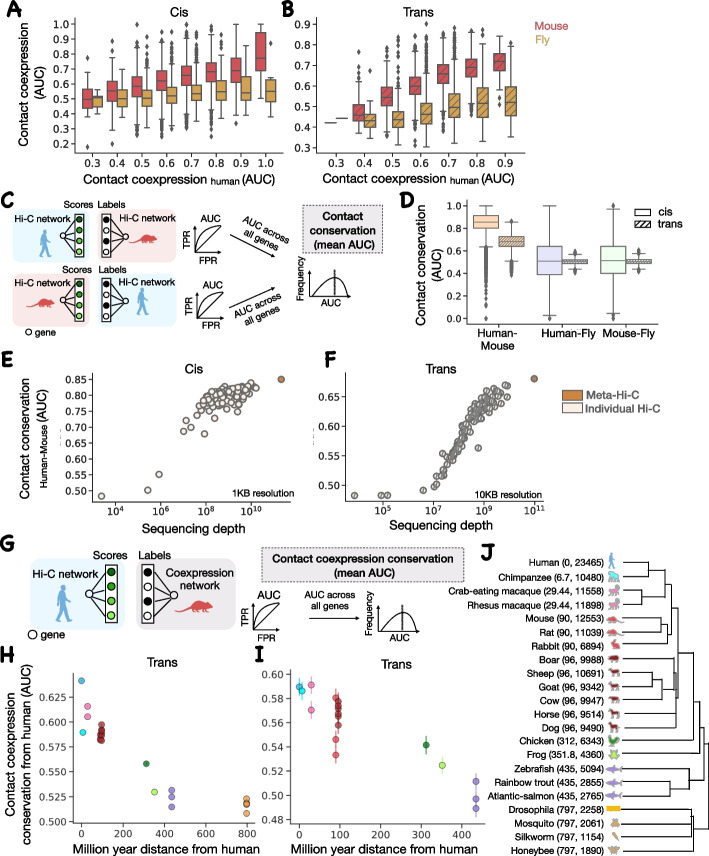
Fig. 4.
Chromatin contacts are conserved across species in both cis and trans. Contact coexpression in cis (A) and trans (B) for 1:1 orthologs in human-mouse and human-fly. C Contact conservation schematic. For each gene, ranked edges in human Hi-C network are used to predict the top 10% of mouse Hi-C network edges. This task is repeated for each gene and in both directions and the average AUC is reported as human-mouse contact conservation. D The distribution of contact conservation score across genes in each direction using the meta-Hi-C network for various pairs of species. human-mouse contact conservation for individual Hi-C network and meta-Hi-C network as a function of sequencing depth in cis (E) and trans (F). G Contact coexpression conservation schematic. For each gene, ranked edges in the human Hi-C network are used to predict the top 1% of mouse coexpression network edges. This task is repeated for each gene and we report the average AUC as mouse contact coexpression conservation with human. H Contact coexpression conservation with human for several species. I Same as (H) but only using the same set of 429 ortholog genes across species. The error bars represent a 68% confidence interval. In cis, the Hi-C network is analyzed at 1-KB resolution, and in trans, the Hi-C network at 10-KB resolution is used for human and mouse and 1-KB resolution for fly. J The dendrogram shows phylogenetic relationships between species used for contact coexpression conservation analysis. Million year distance from human and number of 1:1 orthologs with human is listed in the parenthesis