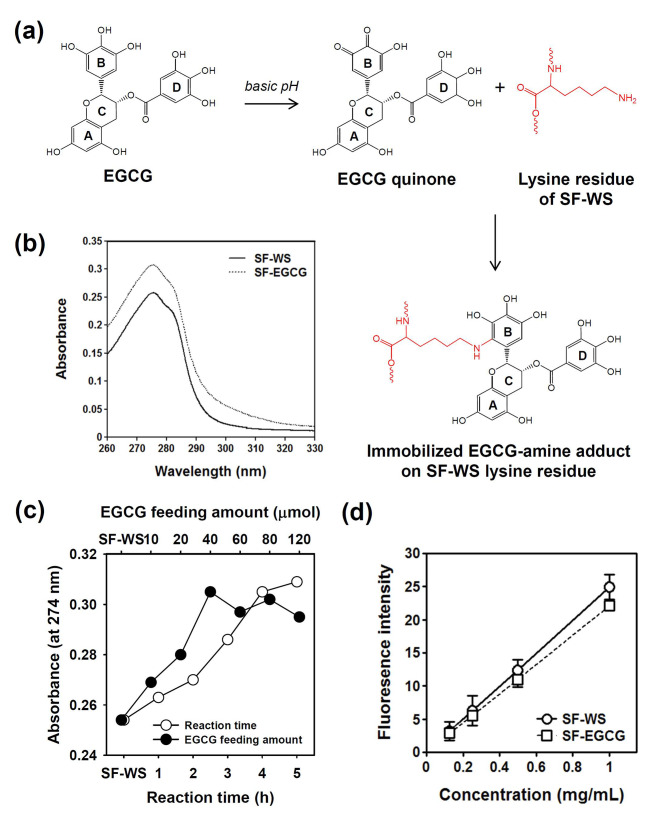
Fig. 1.
(a) Scheme of the SF-EGCG conjugate formation through autoxidation of EGCG at basic pH 7.4 and subsequent conjugation reaction of EGCG quinone with a lysine residue of SF-WS. (b) UV-visible spectra of SF-WS and SF-EGCG solutions at an equal concentration (50 µg/mL). (c) Optimization of EGCG feeding amount and reaction time. Absorbance at 274 nm of SF-EGCG conjugates formed at various reaction time (feeding amount of EGCG = 40 µmol) and various feeding amounts of EGCG (reaction time = 4 h). (d) Fluorescence intensity (λex = 390 nm, λem = 515 nm) of SF-WS and SF-EGCG solutions on primary amine content after 1 min of reaction with fluorescamine assay reagent (n = 8)