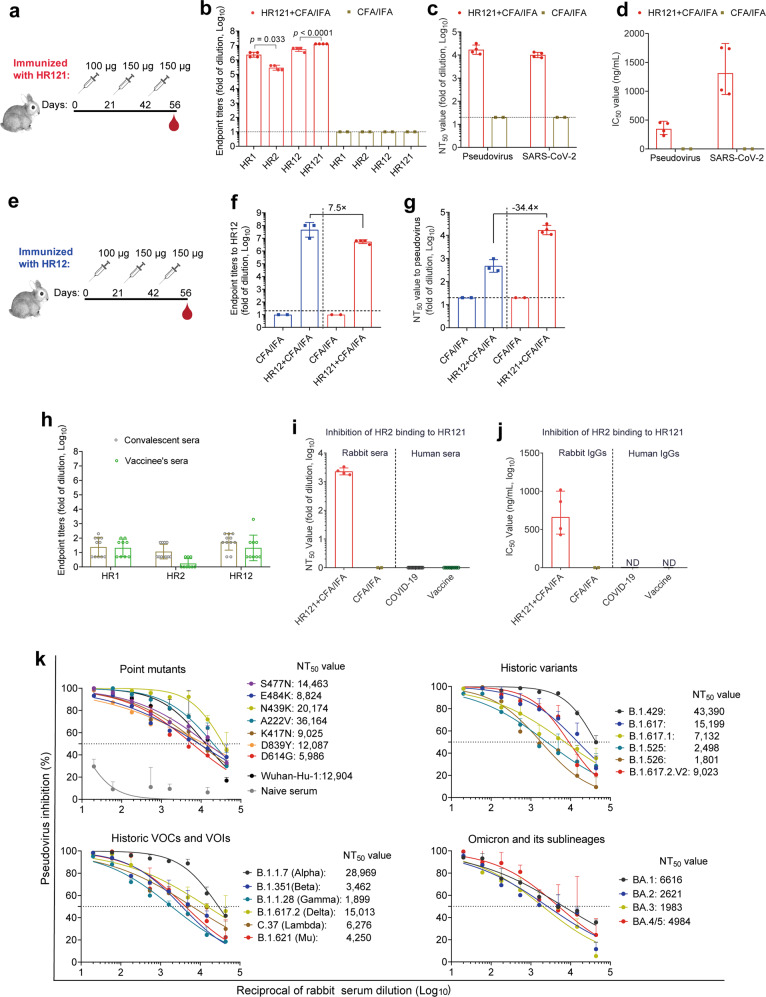
Fig. 2. HR121 induced potent bAbs and nAbs in rabbits against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
a Schematic diagram of rabbit immunization with HR121 formulated with CFA and IFA (n = 4) or CFA/IFA only (n = 2). b Endpoint titers of bAbs to purified SARS-CoV-2 HR proteins in HR121-immunized rabbits. P values were determined by ordinary one-way ANOVA. c, d nAbs to SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus and authentic virus in HR121-immunized rabbits. nAbs in rabbit sera are presented with NT50s (c), and nAbs in IgGs purified from sera with IC50s (d). e Schematic diagram of rabbit immunization with HR12 with CFA/IFA (n = 3) or CFA/IFA only (n = 2). f Comparison of bAbs to HR12 protein between HR12 immunization and HR121 immunization. g Comparison of nAbs to SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus between HR12 immunization and HR121 immunization. h bAbs to HR proteins in sera from human COVID-19 convalescent (n = 11) and vaccinated individuals (n = 9). i, j Inhibitions of HR121 and HR2 binding by sera (i) and IgGs (j) from HR121-immunized rabbits were determined by a competitive ELISA, and inhibitions by sera from human COVID-19 convalescents (n = 11) and vaccinated individuals (n = 9) were also evaluated. ND, not determined. k Dose-dependent curves of rabbit anti-HR121 sera to 23 current SARS-CoV-2 pseudo-variants. The NT50s are marked (dashed lines) and calculated by GraphPad Prism 8.0.1. In b–d, f, g, and h–j, data are presented as geometric mean ± geometric standard deviation (SD), and horizontal dashed lines mean the limit of quantification.