Figure 1.
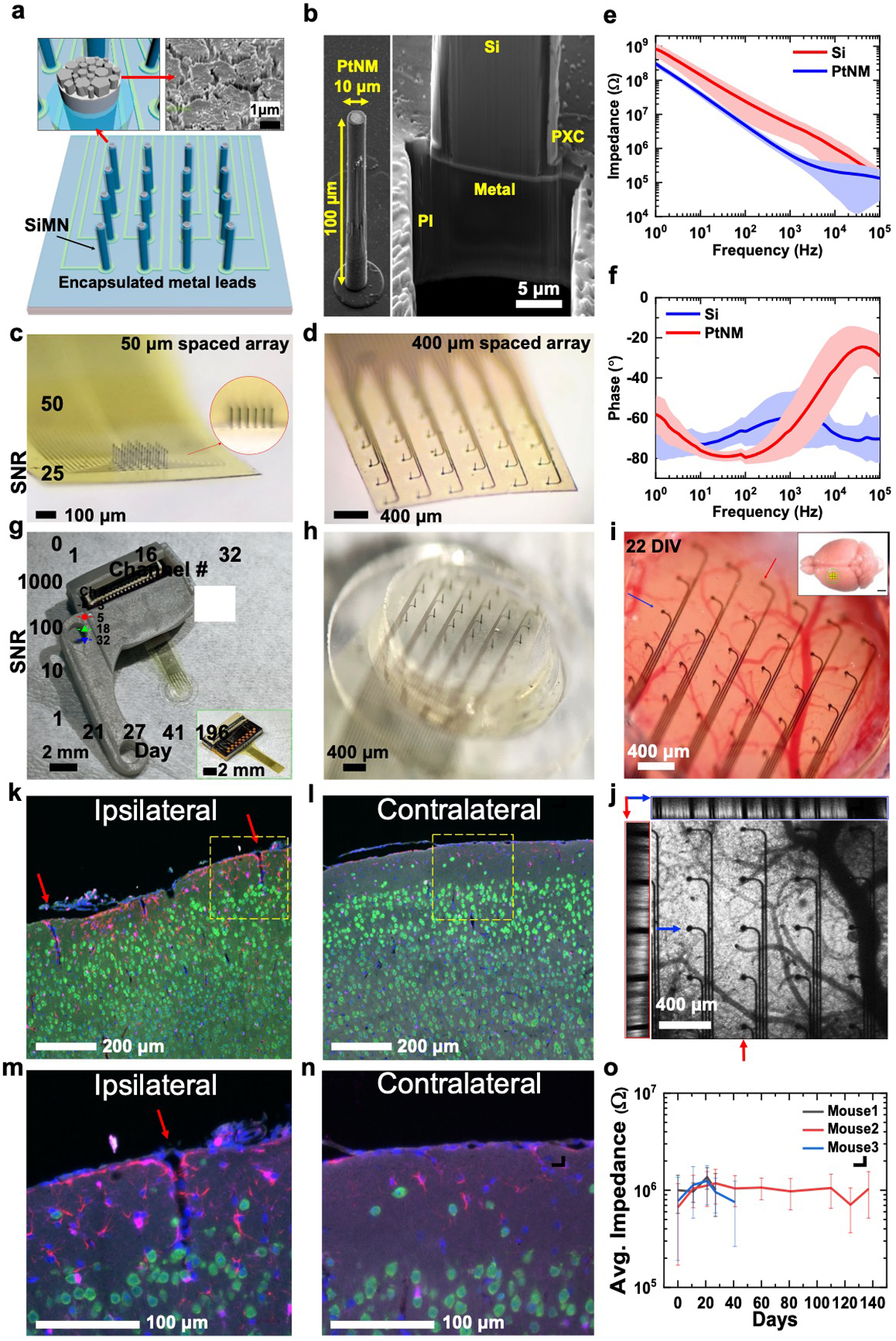
32-channel silicon microneedle array on flexible substrate (SiMNA on flex) for multimodal recording. a) A schematic of a 32-channel SiMNA on flex with polyimide passivating the metal leads and parylene-C passivating the SiMNA (excluding the tips). Inset on the left shows magnified view of the exposed SiMN tip with PtNM coated on Si, and the inset on the right shows the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of the PtNM surface at the tip. b) SEM images (59.8° view) showing a single SiMN with height of 100 μm and diameter of about 10 μm (left), and the FIB-cut cross-section at the base of a single SiMN to demonstrate the underlying 10 μm thick flexible polyimide (PI) substrate supporting the metal lead and the SiMN that are passivated with 1 μm thick parylene-C layer (PXC). c) A magnified optical image of 32-channel SiMNA with 50 μm needle-to-needle spacing. The inset shows the magnified photograph taken from the side of the SiMNA. d) A magnified photograph of 32-channel SiMNA with 400 μm needle-to-needle spacing. e) Impedance plotted against frequency for a Si needle with diameter of 10 μm before (red) and after (blue) coating with PtNM. The average impedance at 1 kHz was 643 ±208 kΩ for PtNM and 5.03 ±3.41 MΩ for Si surface. f) Phase angle plotted against frequency for a SiMN with diameter of 10 μm before (red) and after (blue) coating with PtNM. The average phase angle at 1 kHz was −66.0° ±13.2° for PtNM and −60.4° ±13.4° for Si surface, before PtNM coating. g) A photograph of the device mounted on 3D-printed custom headpost. Inset shows a photograph of a 32-channel SiMNA with 400 μm needle-to-needle spacing bonded to a custom connector PCB before mounting on 3D-printed custom headpost. h) A magnified photograph of the array region mounted on chronic cranial window before implantation. i) A magnified photograph of a 32-channel SiMNA implanted on mouse somatosensory cortex (22 days in vivo). Inset shows the approximate size of the craniotomy at the implantation site (scale bar, 2 mm). j) Two-photon image of the array from i). The left (red box) and the top (blue box) insets show the cross-sectional images taken from the vertical (red arrow, medial-lateral) and horizontal (blue arrow, posterior–anterior) sections. Fluorescence results from pan-neuronal ChR2-EYFP expression in Emx1-Cre; Ai32 mice. k–n) Fluorescence microscopy images of coronal tissue sections stained to visualize cell nuclei (DAPI, blue), neurons (NeuN antibody, green), astrocytes (GFAP antibody, red), and microglia (Iba1 antibody, magenta) from the SiMNA-implanted hemisphere (ipsilateral), and control hemisphere (contralateral) after 73 days in vivo. Red arrows indicate tissue penetration from single SiNM and yellow dashed boxes indicate the magnified regions in m) and n). o) Average impedance of electrically functional SiMNs plotted against days of chronic implantation in 3 different mouse brains.
