Figure 4.
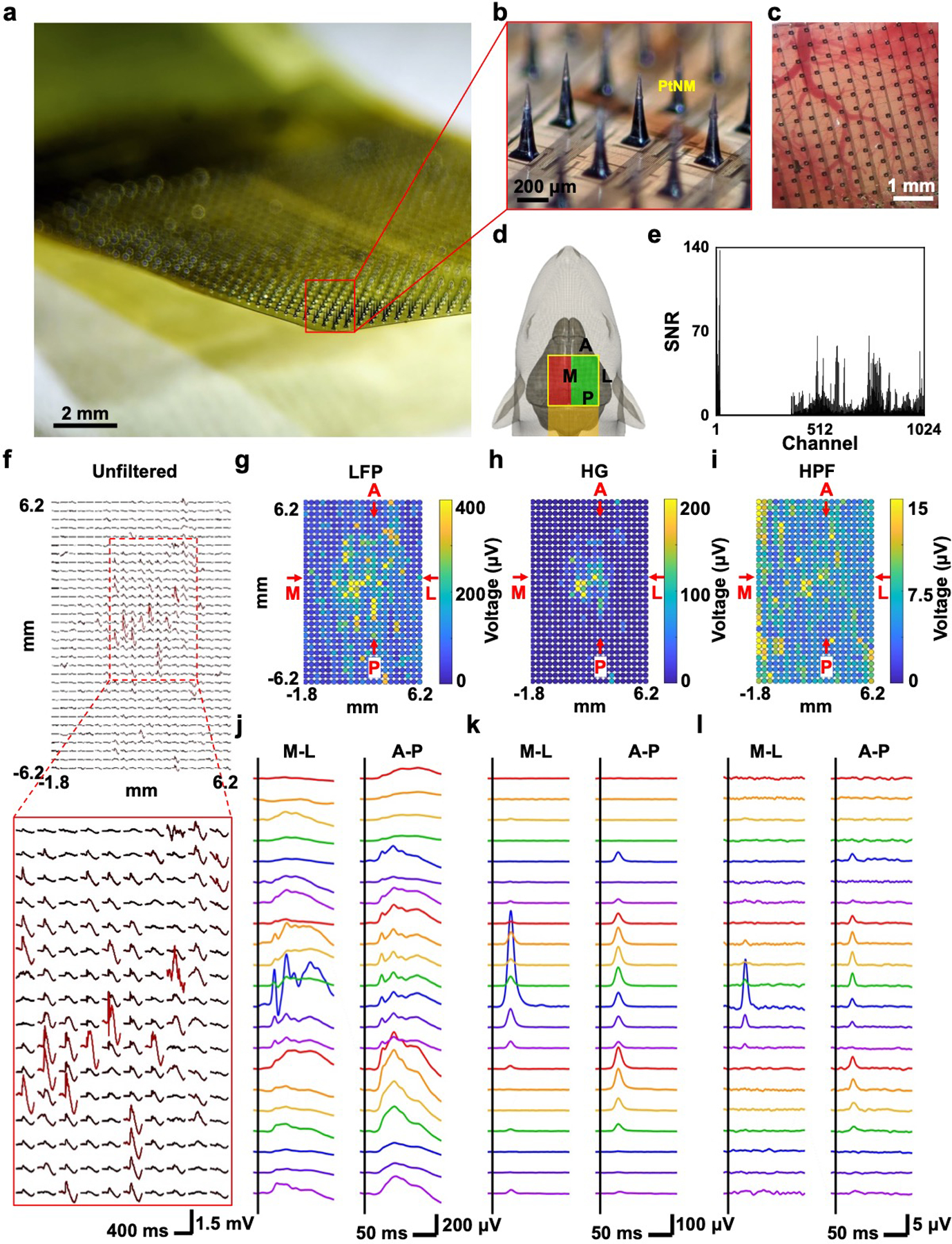
1024-channel silicon microneedle array on flexible substrate (SiMNA on flex) for the detection of in vivo whisker air puff stimulation-evoked responses. a) A photograph of 1024-channel SiMNA on flex rested in mid-air. b) Magnified view of the array with SiMNs with tapered shape with height of about 300 μm and sharp tips coated with PtNM. c) Magnified view of the 1024-channel SiMNA implanted on the right hemisphere of rat brain. d) Schematic of implantation setup. Electrical connection is directed toward the posterior direction of the rat and the SiMNA is implanted in on the right hemisphere. The air puff is aimed on the contralateral whiskers. Green highlight region indicates the successfully implanted SiMN into the cortex, whereas the SiMNs in the red highlighted region are resting atop the rat skull. e) Histogram of SNR of whisker air puff stimulation-evoked LFP responses for 1024 channels (showing 672 channels from the green highlighted region from d) but excluding 352 channels from the red region from d). f) Mapping of unfiltered, trial averaged, stimulation evoked waveforms. g–i) Colormaps of filtered whisker air puff stimulation-evoked LFP, HG, and HPF responses (average of 60 trials, LFP: 1–250 Hz, HG: 70–190 Hz, HPF: 250–3000 Hz). j–l) Filtered waveforms from medial (M)-lateral (L), and anterior (A)-posterior (P) cross-sections from corresponding colormaps in g–i) (average of 60 trials, LFP: 1–250 Hz, HG: 70–190 Hz, HPF: 250–3000 Hz).
