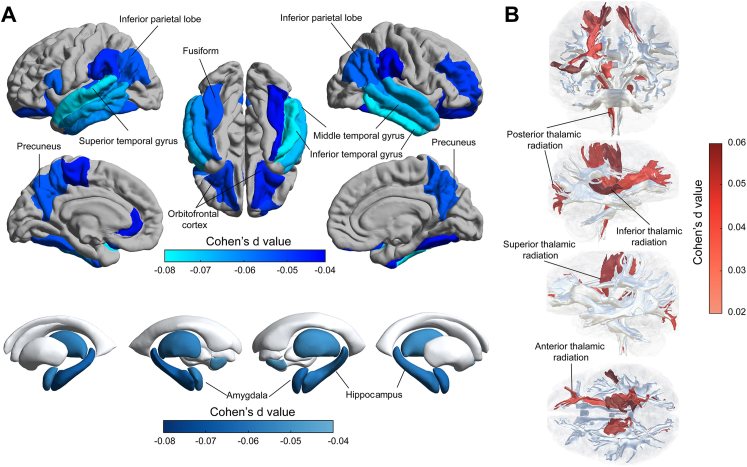
Fig. 3.
The association of hearing performance with brain structure. a. Lower volume of cortical and subcortical regions was associated with poor hearing performance; b. Higher mean diffusivity of white matter tracts was associated with poor hearing performance. The hearing performance was measured using the speech-in-noise test, in which the higher speech-reception-threshold indicated the poorer hearing performance. The association between hearing performance and brain structure were investigated in the multiple linear regression models with the covariates regressed out including age, sex, body mass index, Townsend deprivation index, education qualification, smoking status, drinking status, and imaging scanning sites in the UK Biobank.