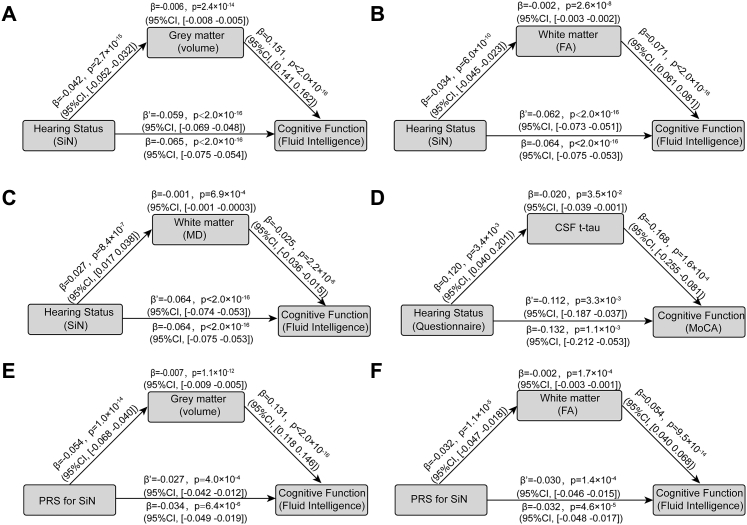
Fig. 5.
Mediation analysis of the association between hearing performance and cognitive function. a. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by brain regions from hearing performance on cognitive function was significant (β = −0.006, P = 2.4 × 10−14, 95%CI: −0.008 to −0.005); b. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by fractional anisotropy of white matter tracts from hearing performance on cognitive function was significant (β = −0.002, P = 2.6 × 10−8, 95%CI: −0.003 to −0.002); c. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by mean diffusivity of white matter tracts from hearing performance on cognitive function was significant (β = −0.001, P = 6.9 × 10−4,95%CI: −0.001 to −0.0003); d. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by CSF tau protein from hearing performance on cognitive function (β = −0.020, P = 3.5 × 10−2, 95%CI: −0.039 to −0.001). e. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by the volume of brain regions from the PRS for hearing performance on cognitive function (β = −0.007, P = 1.1 × 10−12, 95%CI: −0.009 to −0.005). f. Mediation analysis: the mediation implemented by the FA of white matter tracts from the PRS for hearing performance on cognitive function (β = −0.002, P = 1.7 × 10−4, 95%CI: −0.003 to −0.001). The indirect and direct effects and P values were estimated using nonparametric bootstrapping with 10,000 iterations with the “Lavaan” package in R software, version 4.2.0. Abbreviations: SiN, Speech in Noise; CSF, Cerebrospinal Fluid; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; CI, Confidence Interval; FA, Fractional anisotropy; MD, Mean diffusivity; PRS, polygenic risk score.