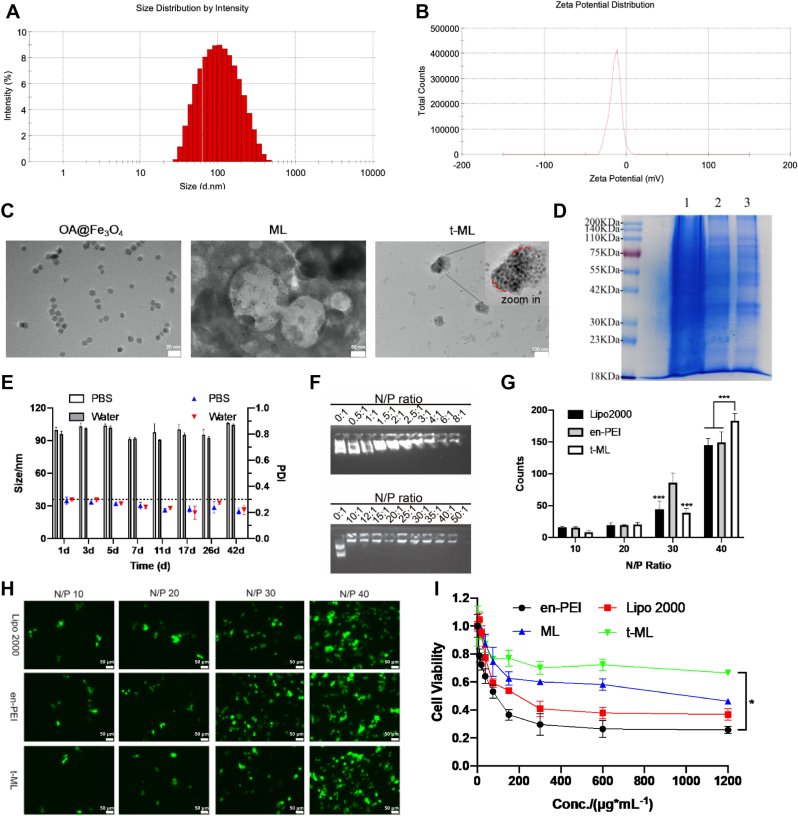
Fig. 1.
Characterization of t-ML. A,B) Size and zeta potential of t-ML; C) TEM images of OA@Fe3O4 (scale bar = 20 nm), ML (scale bar = 50 nm), t-ML (scale bar = 100 nm); D) SDS-PAGE protein analysis of prostate cancer cells (1), prostate cancer cell membranes (2), and t-ML (3); E) the stability test results of t-ML in PBS or ultrapure water in 42 days (n = 3, mean ± SD); F) Results of agarose gel electrophoresis (pEGFP: 1 μg); G) statistical analysis of the gene transfection assay (n = 3, mean ± SD, multiple t-test, ∗∗∗P < 0.001); H) gene transfection fluorescence images of t-ML at different N/P ratios (bars: 50 μm); I) CCK-8 assay of the toxicity of Lipo 2000, en-PEI, ML and t-ML (n = 3, mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, ∗P < 0.05).