FIGURE 4.
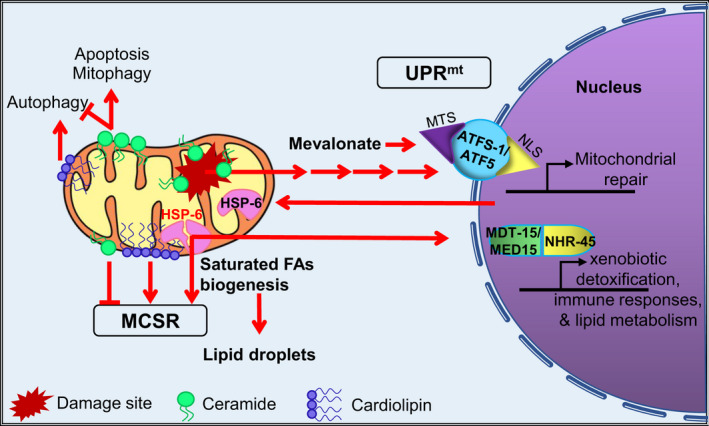
Lipids surveillance in mitochondria. At least two pathways, the UPRmt and the MCSR, involve monitoring the levels of various lipid species. For example, sites of mitochondrial damage are marked by ceramides, which activate the UPRmt. Mevalonate, a precursor of many biologically important molecules, such as cholesterol, ubiquinones, and heme a, is also implicated in UPRmt regulation. Accumulation of ceramides on the outer mitochondrial membrane promotes apoptosis and mitophagy while inhibiting autophagy. Ceramides also block the MCSR, a cytosolic stress response that is triggered by mitochondrial dysfunction. In contrast, cardiolipin (a lipid largely restricted to mitochondria in eukaryotes) activates the MCSR and promotes autophagy. Disruption of HSP‐6 also triggers the formation of lipid droplets, a stress response to minimize lipotoxicity, and activates a xenobiotic response mediated by MDT‐15/NHR‐45. Abbreviations: FA—fatty acid, MTS—mitochondrial targeting sequence, and NLS—nuclear localization signal
