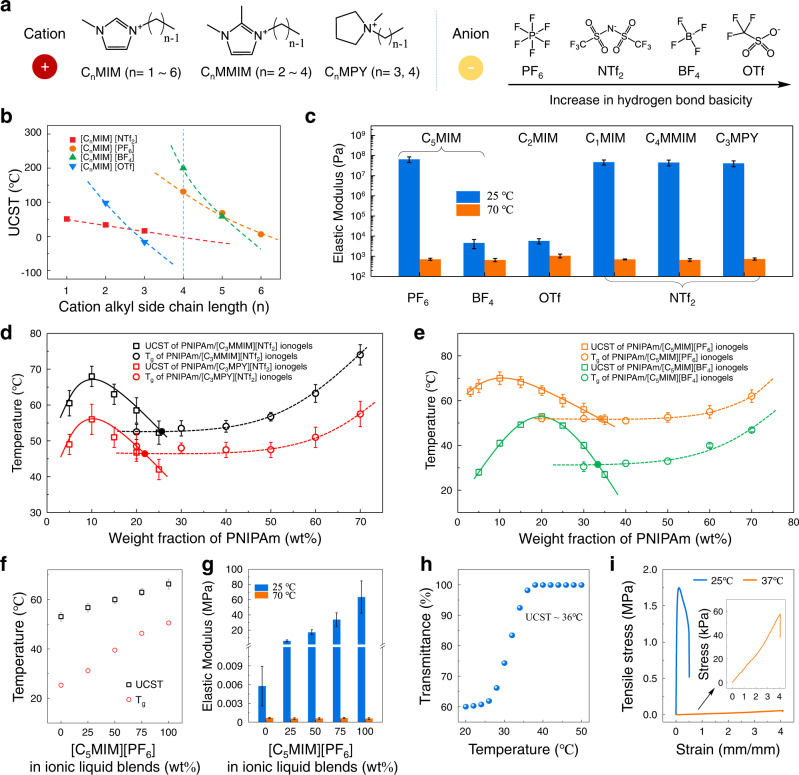
Fig. 3. Structural effects of ILs on the Berghmans’ point.
a Molecular structures of cations and anions of ILs used in this work. b UCST of ionogels with respect to the molecular structure ILs. c Mechanical characterization of PNIPAm ionogels using different ILs as solvent with elastic modulus extracted from the initial stress–strain curves (the UCST of ionogels from left to right are 66.3 °C, 53.2 °C, 98 °C, 51 °C, 52 °C and 47 °C, respectively). d Effect of cation in ILs on the phase diagram of the ionogels. e Effect of anion in ILs on the phase diagram of the ionogels. f Tuning the UCST and Tg of the ionogels by varying the mixing ratio of anions in ionic liquids blends ([C5MIM][PF6]/[C5MIM][BF4]). g Thermoresponsive stiffness-changing properties of the ionogels in f. h Temperature dependence of transmittance at 658 nm for PNIPAm ionogels with certain feed ratios of constituents (PNIPAm content: 32 wt%, ionic liquid blends: [C5MIM][PF6]:[C5MIM][BF4] = 1:3). i Tensile stress–strain curves of PNIPAm ionogels at 25 °C and 37 °C, respectively. The elastic modulus of ionogels at 25 °C and 37 °C are 50.2 MPa and 11.4 kPa, respectively. All error bars represent the mean ± standard deviations (n ≥ 3 independent experiments).